108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

开发和验证 9 种趋化因子的免疫相关分类器,用于预测 I-III 期结直肠癌患者的术后复发
Authors Xu G, Zhou Y, Zhou F
Received 17 May 2018
Accepted for publication 11 July 2018
Published 1 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4051—4064
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S174452
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Introduction: Chemokines are closely related with tumor immunity, progression,
and metastasis. We aimed to construct a multi-RNA classifier of chemokine
family genes for predicting tumor recurrence in stage I–III patients with
colorectal cancer (CRC) after operation.
Patients and
methods: By analyzing microarray data, the
Cox regression analysis was conducted to determine survival-related chemokine
family genes and develop a multi-RNA classifier in the training set. The
prognostic value of this multi-RNA classifier was further validated in the
internal validation and external independent sets. Receiver operating
characteristic curves were used to compare the prediction ability of the
combined model of this multi-RNA classifier and stage, and this multi-RNA classifier
and stage alone.
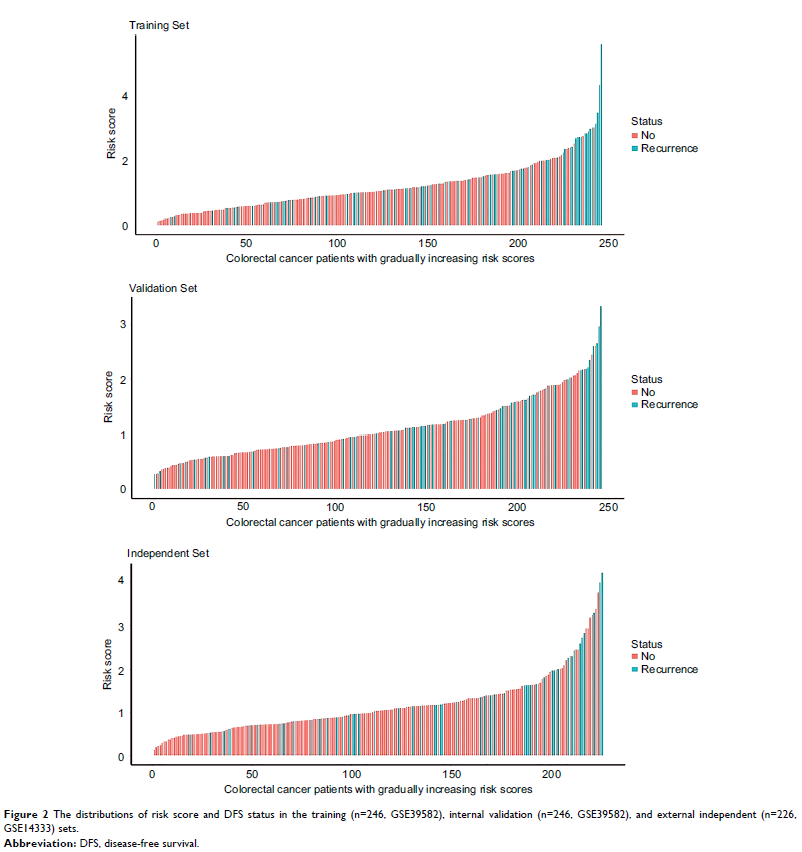
Results: Nine survival-related chemokines were identified in the training
set. We identified a nine-chemokine classifier and classified the patients as
high-risk or low-risk. Compared with CRC patients with high-risk scores, CRC patients
with low-risk scores had longer disease-free survival in the training
(HR=2.353, 95% CI=1.480–3.742, P <0.001),
internal validation (HR=2.389, 95% CI=1.428–3.996, P <0.001), and external
independent (HR=3.244, 95% CI=1.813–5.807, P <0.001)
sets. This nine-chemokine classifier was an independent prognostic factor in
these datasets (P <0.05). The combined model of
this nine-chemokine classifier and tumor stage may tend to have higher accuracy
than stage alone in the training (area under curve 0.727 vs 0.626, P <0.01), internal validation
(0.668 vs 0.584, P =0.03), and external
independent (0.704 vs 0.678, P >0.05) sets.
This nine-chemokine classifier may only be applied in Marisa’s C2, C5, and C6
subtypes patients.
Conclusion: Our nine-chemokine classifier is a reliable prognostic tool for
some specific biological subtypes of CRC patients. It might contribute to guide
the personalized treatment for high-risk patients.
Keywords: classifier, colorectal cancer, chemokine, survival analysis, risk
classification, microarray