108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NOP7 与 β-连环蛋白相互作用并激活肝细胞癌细胞中的 β-连环蛋白/TCF 信号
Authors Wu N, Zhao J, Yuan Y, Lu C, Zhu W, Jiang Q
Received 4 February 2018
Accepted for publication 23 June 2018
Published 1 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6369—6376
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164601
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
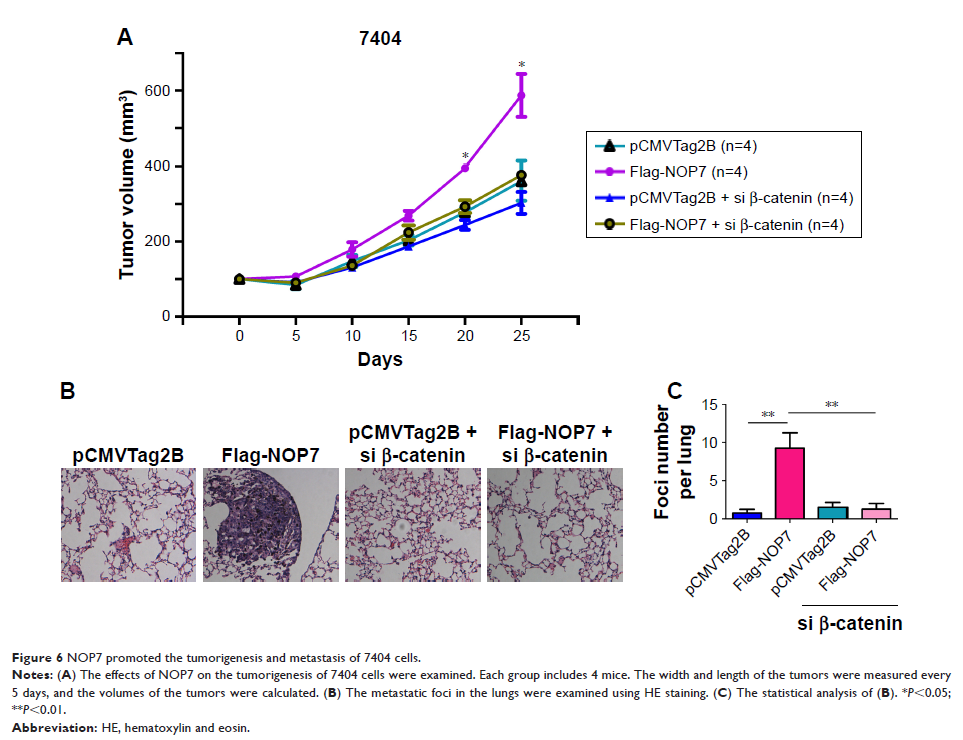
Background: The hyperactivation of β-catenin signaling is frequently observed
in clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples. Further understanding the
mechanisms involved in activating β-catenin/TCF signaling would benefit the
treatment of HCC.
Method and
results: Here, it was found that NOP7 was a
binding partner of β-catenin. NOP7 strengthened the interaction between
β-catenin and TCF4, which led to the activation of β-catenin/TCF signaling. The
upregulation of NOP7 in HCC promoted the growth (in both liquid culture and
soft agar) and migration of HCC cancer cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, we have demonstrated the oncogenic functions of
NOP7 in HCC, suggesting that targeting NOP7 would benefit the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, NOP7, β-catenin/TCF pathway, cell
growth, cell migration