108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

敲除 CLDN6 可抑制子宫内膜癌细胞系 HEC-1-B 中 PI3K/AKT/mTOR 信号通路的细胞增殖和迁移
Authors Cao X, He GZ
Received 18 May 2018
Accepted for publication 10 August 2018
Published 1 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6351—6360
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S174618
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Backgroud: Dysregulation of claudin-6 (CLDN6) expression in cancers has been
widely documented. However, no study has reported a complete mechanistic
understanding of CLDN6 regulation and function in endometrial carcinoma (EC)
progression. In the current study, we aimed to assess the expression and
biological functions of CLDN6 in EC.
Methods: Firstly, the expression level of CLDN6 in EC was measured based on
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Then, qRT-PCR and western blotting
were implemented to detect the expression levels of CLDN6 in 82 pairs of EC
tissues and corresponding non-tumor tissues, as well as EC cell line HEC-1B.
After knockdown of CLDN6, with the attempt to assess whether CLDN6 reduction
had positive effects on the cell proliferation, clone formation, invasion and
migration abilities of HLC-1Bs, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (24, 48, 72
and 96 hours post-transfection), clone experiment, and invasion and migration
assays were conducted. Through western blotting analysis, CLDN6-mediated
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway was evaluated.
Results: Based on the data of TCGA database, clinical patients and cell
line HEC-1B, CLDN6 was up-regulated in EC compared with normal. Univariate as
well as multivariate COX analysis indicated that CLDN6 expression can act as an
independent prognostic factor for overall survival of EC. Further, knockdown of
CLDN6 significantly inhibited HEC-1B cell proliferation, suppressed the colony
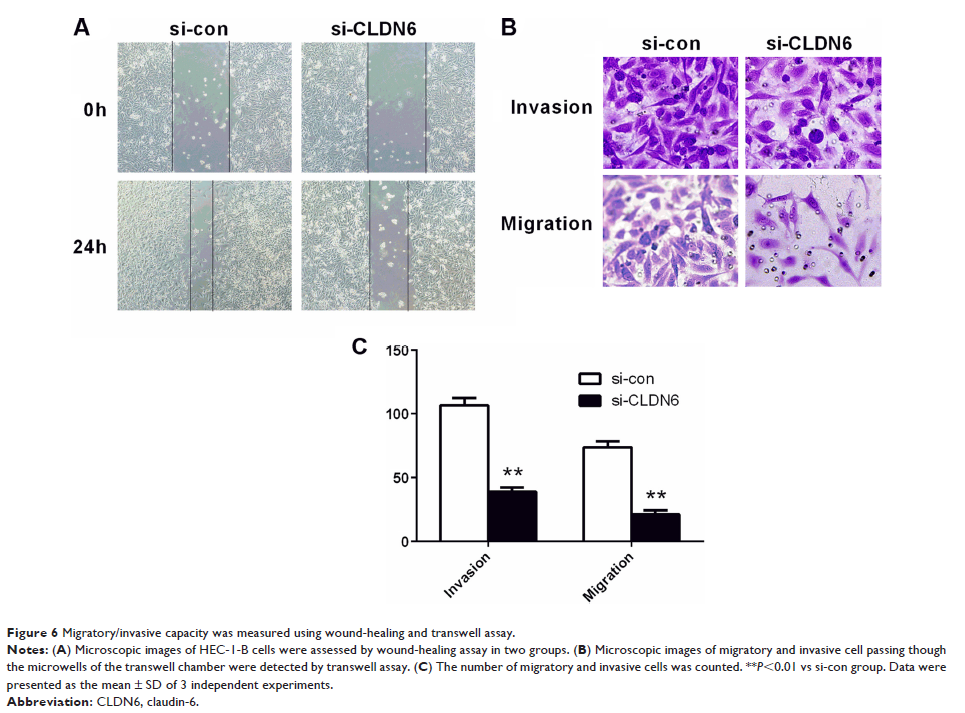
numbers of HEC-1-B cells, and restrained the invasive and migratory ability of
HEC-1-B cells. Importantly, through western blot analysis, we found that
inhibition of CLDN6 remarkably decreased p-AKT, p-PI3K, and mTOR expression
level in EC HEC-1B cell line.
Conclusion: Our data underscore the significance of CLDN6 in EC progression,
and CLDN6 is a new candidate oncogene in EC. Our findings propose that
targeting CLDN6 might offer future clinical utility in EC.
Keywords: endometrial carcinoma, CLDN6, knockdown, proliferation, PI3K/AKT
pathway, prognostic, invasion