108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

九里香抑制肿瘤细胞源性培养基诱导的血管生成并抑制斑马鱼和内皮细胞中的 AKT 活化
Authors Long W, Wang M, Luo X, Huang G, Chen J
Received 10 July 2017
Accepted for publication 14 May 2018
Published 24 September 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3107—3115
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S145956
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Introduction: Lung cancer is a major cancer type and a leading cause of cancer-related death. Angiogenesis plays a crucial role in lung cancer pathogenesis and its inhibition is beneficial to patients.
Materials and methods: Murrangatin, a natural product, can inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells, so herein we investigated its anti-angiogenic effects in transgenic zebrafish TG (fli1: EGFP) and in lung cancer cell-induced angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
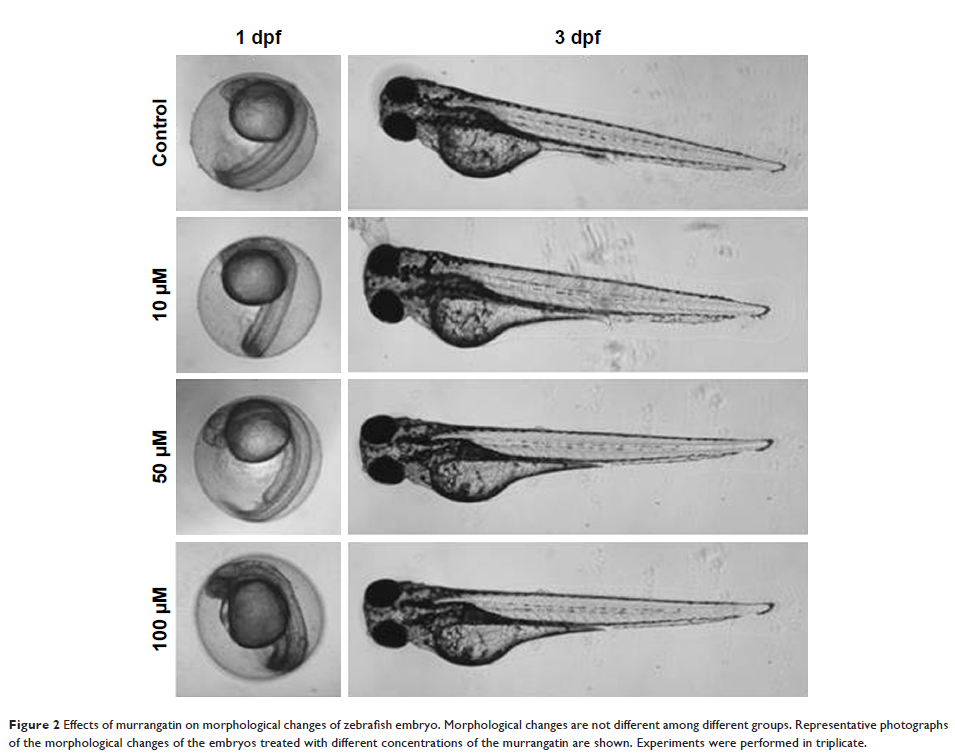
Results: We found that murrangatin strongly inhibited the growth of subintestinal vessels in zebrafish embryos and tumor conditioned media-induced angiogenic phenotypes including cell proliferation, cell invasion, cell migration, and tube formation. Additionally, murrangatin greatly attenuated conditioned medium-induced AKT phosphorylation, but not extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation.
Discussion and conclusion: These findings indicate that murrangatin can inhibit tumor-induced angiogensis, at least in part through the regulation of AKT signaling pathways. Murrangatin may, therefore, be a potential candidate for the development of new anti-lung-cancer drugs.
Keywords: anti-angiogenesis, murrangatin, conditioned medium, zebrafish, HUVECs, AKT