108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

结直肠癌联合疗法使用药物和基因共同递送、靶向聚(乙二醇)-ε-聚(己内酯)的纳米载体
Authors Wang Z, Wei Y, Fang G, Hong D, An L, Jiao T, Shi Y, Zang A
Received 29 May 2018
Accepted for publication 31 July 2018
Published 24 September 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3171—3180
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175614
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: Combination therapy is a promising strategy to treat cancer due to the synergistic effects. The drug and gene co-delivered systems attract more attention in the field of combination therapy.
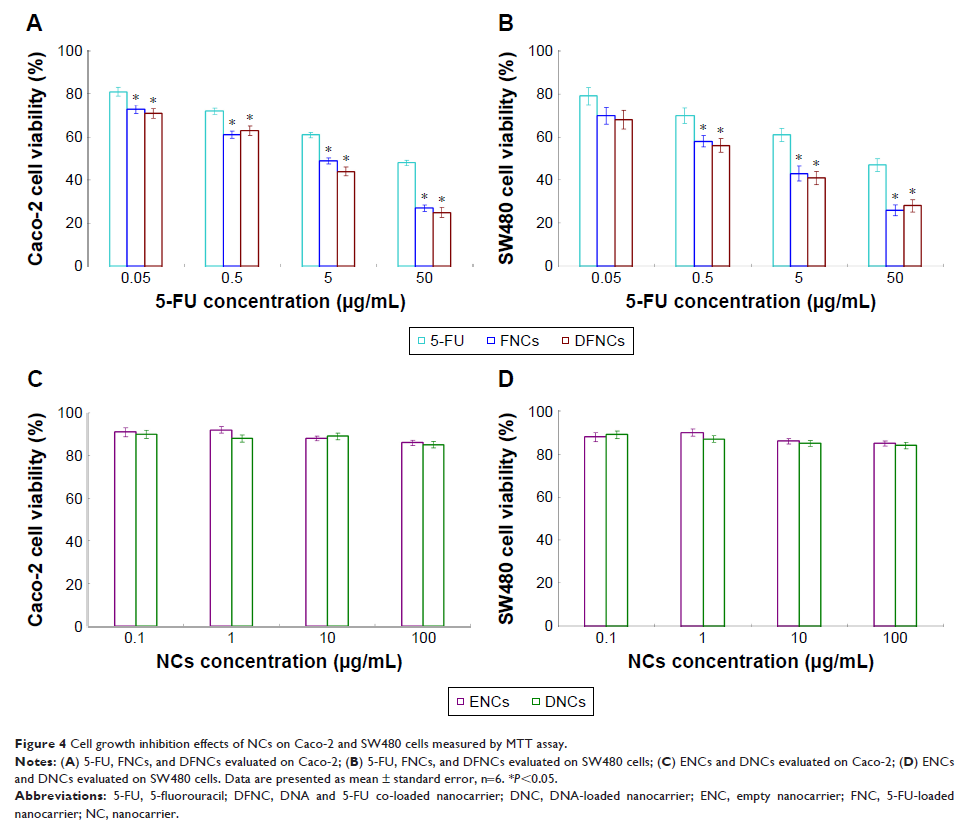
Materials and methods: In the present research, poly(ethylene glycol)-ε-poly(caprolactone) block copolymer was used for the co-loading of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and gene. The physicochemical characteristics, in vitro and in vivo anticancer, and gene transfection efficiency were tested on colon cancer cells and tumor-bearing mice.
Results: 5-FU and gene co-loaded nanocarriers had a size of 145 nm. In vivo gene delivery results showed about 60% of gene-positive cells. Tumor volume of nanocarrier groups at day 21 was around 320 mm3, which is significantly smaller compared with free 5-FU group (852 mm3) and control group (1,059 mm3). The maximum 5-FU plasma concentration in nanocarrier groups (49 µg/mL) was significantly greater than free 5-FU (13 µg/mL). At 24 hours, drug level of nanocarrier groups was about 2.8 µg/mL compared with 0.02 µg/mL of free 5-FU.
Conclusion: The resulting nanocarriers co-loaded with the anticancer drugs and genes could be considered as a promising nanomedicine for colorectal cancer therapy.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, gene therapy, combination therapy, cytotoxicity, transfection efficiency