108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

缺氧诱导因子稳定剂在慢性肾脏病患者贫血治疗中的作用
Authors Zhong H, Zhou T, Li H, Zhong Z
Received 31 May 2018
Accepted for publication 6 August 2018
Published 18 September 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3003—3011
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rammohan Devulapally
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to analyze the effects of
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) stabilizers on anemia in non-dialysis-dependent
(NDD) and dialysis-dependent (DD) chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
Methods: Published studies were extracted from PubMed, China Biological
Medicine Database (CBM), Wanfang database, and Cochrane Library on March 10,
2018, and relevant studies were pooled and included in a meta-analysis. Data on
hemoglobin (Hb), ferritin, and hepcidin levels, total iron-binding capacity
(TIBC), and incidence of adverse events (AEs) were extracted and pooled using
Review Manager Version 5.3.
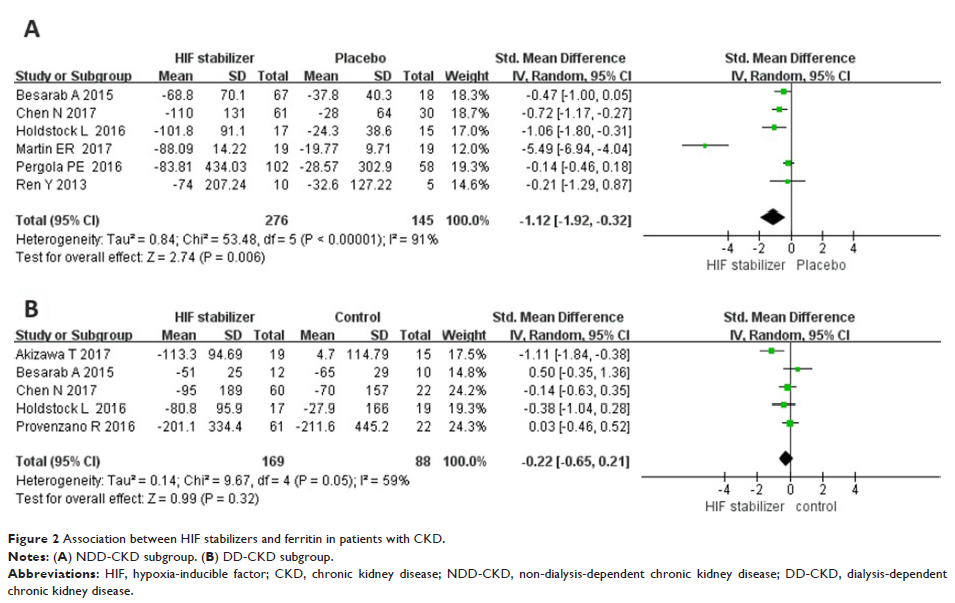
Results: Data from nine selected studies were extracted. Meta-analysis of
the included studies showed that HIF stabilizers reduced ferritin and hepcidin
levels and increased Hb level and TIBC in NDD-CKD patients. However, HIF
stabilizers only increased TIBC, and did not affect ferritin, hepcidin, and Hb
levels in DD-CKD patients. Furthermore, no notable differences in AEs and
severe AEs between NDD-CKD and DD-CKD patients were detected.
Conclusion: HIF stabilizers are effective for the treatment of anemia in
NDD-CKD patients and safe for short-term use.
Keywords: hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizer, anemia, chronic kidney
disease, meta-analysis