108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Olaparib 作为单药治疗 BRCA2 基因突变的难治性肝内胆管细胞癌:一份病例报告
Authors Cheng Y, Zhang J, Qin SK, Hua HQ
Received 11 June 2018
Accepted for publication 6 August 2018
Published 18 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5957—5962
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S176914
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Abstract: Olaparib is an oral poly ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitor with
activity in germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 (BRCA1/2)-associated breast and ovarian
cancers. There is no report about treatment with olaparib in BRCA1/2-mutated
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. This study is to observe the efficacy and
safety of olaparib monotherapy in the refractory BRCA1/2-mutant intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient. The clinical record of a patient with
BRCA2-mutated refractory advanced ICC treated with olaparib was analyzed. The
patient was administered with olaparib (400 mg orally twice daily) and followed
up for 11 months. The clinical tumor response was evaluated after 4 weeks of
olaparib treatment, and then every 8 weeks (two treatment cycles). The patient
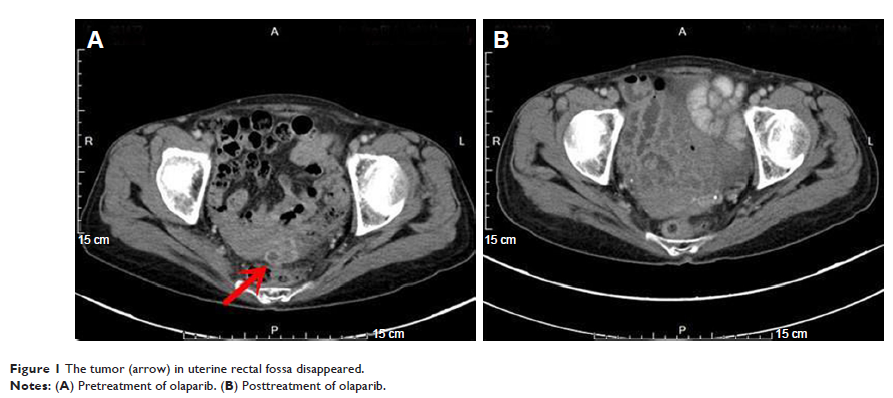
achieved partial response confirmed by the computed tomography and the tumor
marker CA19.9, CA50, and CA125 levels decreased significantly as an outcome of
the treatment. The quality of life improved significantly. Major adverse events
were fatigue, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and anemia, which were manageable
with medication. The patient is still receiving treatment. Olaparib in the
treatment of BRCA2-mutation-associated refractory advanced ICC patent is
effective, and the adverse effects are tolerated. Large-scale studies should be
conducted to further the adoption of genomic profiling, which may help
clinicians identify suitable biomarkers for therapy of ICCs. A possible line of
therapy is often extrapolated from case reports or small case series.
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas, ICC, olaparib, BRCA1/2