108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对于 IIIA-N2 NSCLC 患者,PLNR≤20% 可能是源自 PORT 的益处: 一项大型以人群为基础的研究
Authors Shang X, Li Z, Lin J, Wang H, Wang Z
Received 11 May 2018
Accepted for publication 29 June 2018
Published 17 September 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3561—3567
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S173856
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: Our study was to evaluate the influence of positive lymph nodes
ratio (PLNR) on survival for patients with pathological stage IIIA-N2 non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after receiving postoperative radiotherapy (PORT).
Patients and
methods: The chi-squared test was used to
compare the patient baseline characteristics. Cox proportional hazard model was
used to analyze the influence of different variables on overall survival (OS).
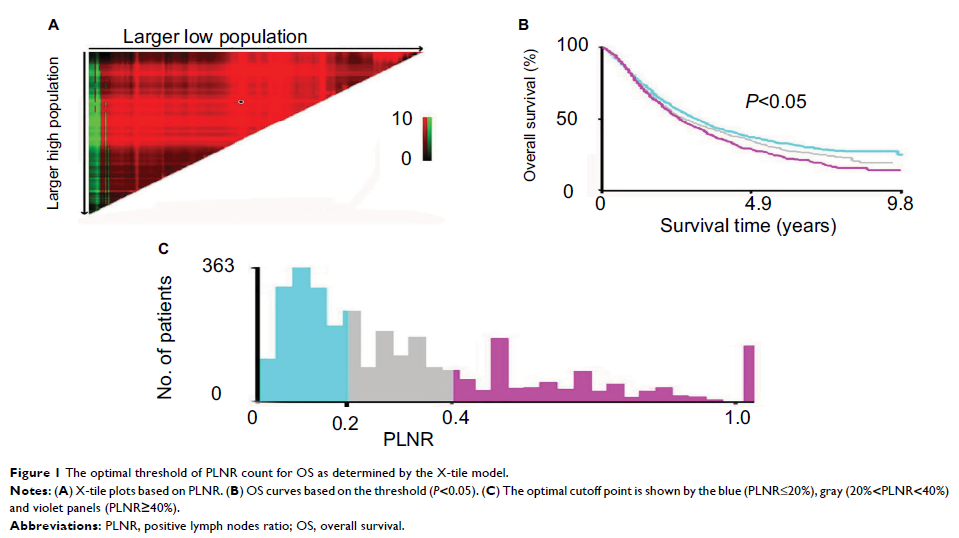
X-tile model was applied to determine the cutoff values of PLNR. Kaplan–Meier
method and log-rank test were used to compare survival differences. Based on different
cutoff values of PLNR, Cox proportional hazard model was also used to analyze
the influence factors on OS.
Results: Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that PLNR (P =0.001) and PORT (HR=1.283; 95%
CI 1.154–1.426; P <0.001) were
significant independent prognostic factors for OS in patients with resected
IIIA-N2 NSCLC. The X-tile model was used to screen three different cutoff
values including PLNR≤20%, 20%40%. Based on these different cutoff values, we
found that patients with PLNR≤20% receiving PORT have a better OS (P =0.007). Further multivariable
analysis showed that PORT is an independent prognostic factor of OS only for
patients with PLNR≤20% (HR=1.328; 95% CI 1.139–1.549; P <0.001).
Conclusion: PLNR≤20% may be a prognostic factor for patients with IIIA-N2
NSCLC receiving PORT.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, postoperative radiotherapy, positive
lymph node ratio, OS, prognosis, X-tile model