108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

神经性地塞米松与罗哌卡因用于胸椎旁阻滞选择性胸廓切开术术后镇痛的疗效:一项随机双盲安慰剂对照试验
Authors Mao Y, Zuo YM, Mei B, Chen LJ, Liu XS, Zhang Z, Gu EW
Received 31 January 2018
Accepted for publication 15 May 2018
Published 11 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1811—1819
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S164225
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr E Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy of perineural dexamethasone with ropivacaine in multimodal analgesia for thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB) in patients undergoing elective thoracotomy.
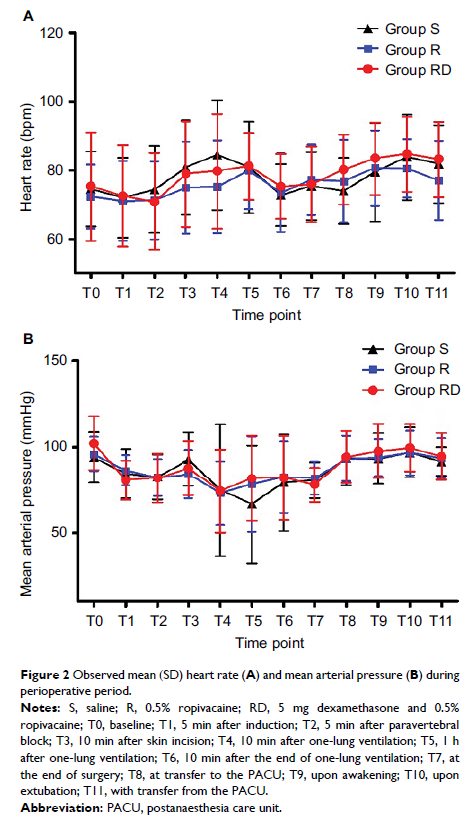
Patients and methods: Ninety-six patients undergoing thoracotomy were enrolled in this trial and randomized to adjuvant therapy for TPVB: group S (saline), group R (0.5% ropivacaine), or group RD (5 mg dexamethasone and 0.5% ropivacaine). Postoperative analgesia, recovery duration, and chronic pain were recorded.
Results: Groups R and RD spent less time in the postanaesthesia care unit, had earlier out-of-bed activity, and had shorter postoperative hospital stays compared with group S. The RD group regained consciousness faster and had lower acute pain scores and used less patient-controlled analgesia during the first 72 h after surgery compared with group S. Postthoracotomy pain was decreased in group RD (19.0%) compared with group S (47.6%) 3 months postoperatively, p = 0.050.
Conclusion: Perineural dexamethasone with ropivacaine for TPVB improves postoperative analgesia quality, reduces recovery time, and may decrease the incidence of chronic pain after thoracotomy with an opioid-based anesthetic regimen.
Keywords: chronic pain, dexamethasone, nerve block, thoracotomy