108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

奈达铂与顺铂治疗恶性胸腔积液的疗效和毒性比较
Authors Zhong LZ, Xu HY, Zhao ZM, Zhang GM, Lin FW
Received 16 March 2018
Accepted for publication 24 May 2018
Published 5 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5509—5512
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S168391
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
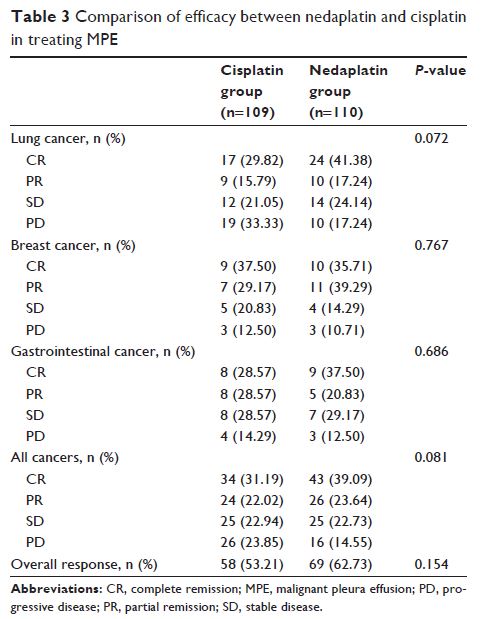
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of nedaplatin versus cisplatin in treating malignant pleural effusion (MPE) caused by cancers.
Methods: The clinical data of 219 MPE patients treated from January 2013 to December 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. Intrapleural infusion with nedaplatin 80 mg/m2 (n=110) or with cisplatin 40 mg/m2 (n=109) were used as the treatment.
Results: There was no significant difference in the overall response rate between the nedaplatin group (62.73%) and the cisplatin group (54.13%) (P =0.154). The nedaplatin group had significantly lower rates of gastrointestinal side effects and significantly less incidence of increased serum creatinine levels in comparison with the cisplatin group. The overall rate of toxicity in the nedaplatin group (40.00%) was significantly lower than in the cisplatin group (78.90%) (P <0.001).
Conclusion: The efficacy of pleural perfusion with nedaplatin is noninferior to cisplatin in treating malignancy-induced MPE. Nedaplatin is associated with less toxicity in comparison with cisplatin.
Keywords: malignant pleural effusion, pleural perfusion, platinum-based drug, toxicity