109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

与肝细胞癌的发展和预后不良相关联的 ADAMTS5 蛋白迷失显示
Authors Li C, Xiong Y, Yang X, Wang L, Zhang S, Dai N, Li M, Ren T, Yang Y, Zhou SF, Gan L, Wang D
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 1773—1783
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S77069
Received 5 November 2014, Accepted 26 January 2015, Published 24 March 2015
Abstract: Altered
expression of ADAMTS5 is associated with human carcinogenesis and tumor
progression. However, the role of ADAMTS5 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is
unclear. This study analyzed ADAMTS5 expression in HCC tissues and tested for
association with clinicopathological and survival data from HCC patients and
then explored the role of ADAMTS5 in HCC cells in vitro. Paraffin blocks from
48 HCC patients were used to detect ADAMTS5 and vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) expression and microvessel density (MVD). A normal liver cell
line and HCC cell lines were used to detect ADAMTS5 expression and for ADAMTS5
manipulation. ADAMTS5 cDNA was stably transfected into HCC cells and ADAMTS5
expression assessed by Western blot analysis. Tumor cell-conditioned growth
medium was used to assess human umbilical vein endothelial cell migration and
Matrigel tube formation. Xenograft assay was performed to determine the role of
ADAMTS5 in vivo. The data showed that the expression of ADAMTS5 was reduced in
HCC, which was inversely associated with VEGF expression, MVD, and tumor size
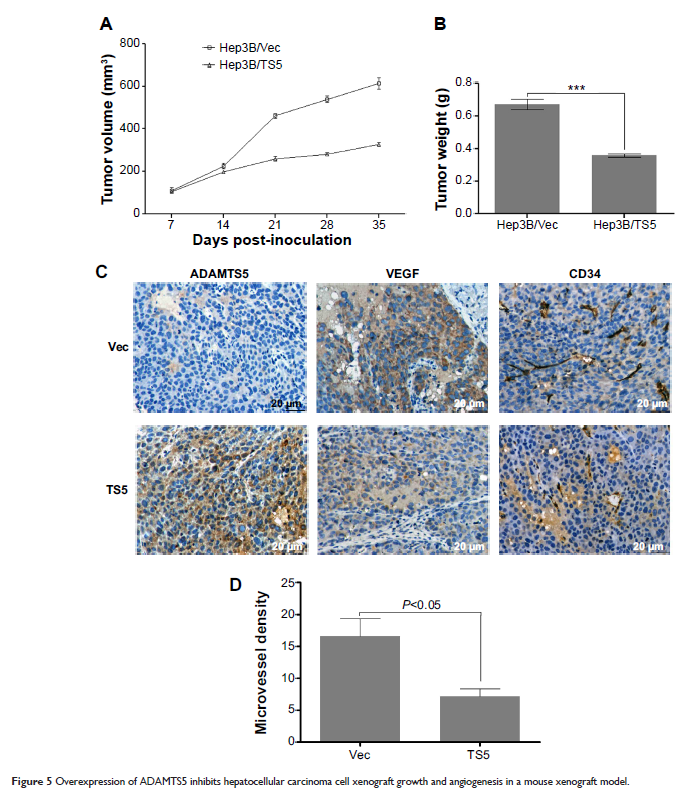
and associated with poor overall survival of HCC patients. Lentivirus -mediated ADAMTS5
expression significantly inhibited tumor angiogenesis by downregulating in
vitro expression of VEGF and inhibiting migration and tube formations, and also
inhibited tumor growth and VEGF expression and reduced MVD in vivo in a mouse
xenograft model. Taken together, these results suggest that ADAMTS5 plays a
role in suppression of HCC progression, which could be further studied as a
promising novel therapeutic target and a potential prognostic marker in HCC.
Keywords: A disintegrin and
metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5, tumor angiogenesis, tumor cell
xenograft