109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
DAPK 启动子高甲基化在肺癌中的临床意义: 一项综合分析
Authors Li Y, Zhu M, Zhang X, Cheng D, Ma X
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 1785—1796
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S78012
Received 23 November 2014, Accepted 6 January 2015, Published 24 March 2015
Abstract: Death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK) is an important
serine/threonine kinase involved in various cellular processes, including
apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation. DAPK expression and activity
are deregulated in a variety of diseases including cancer. Methylation
of the DAPK gene is common in many
types of cancer and can lead to loss
of DAPK expression. However, the association between DAPK promoter hypermethylation
and the clinicopathological significance of lung cancer remains unclear.
In this study, we searched the MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus
databases, systematically investigated the studies of DAPK promoter
hypermethylation in lung cancer and quantified the association
between DAPK promoter
hypermethylation and its clinicopathological significance by
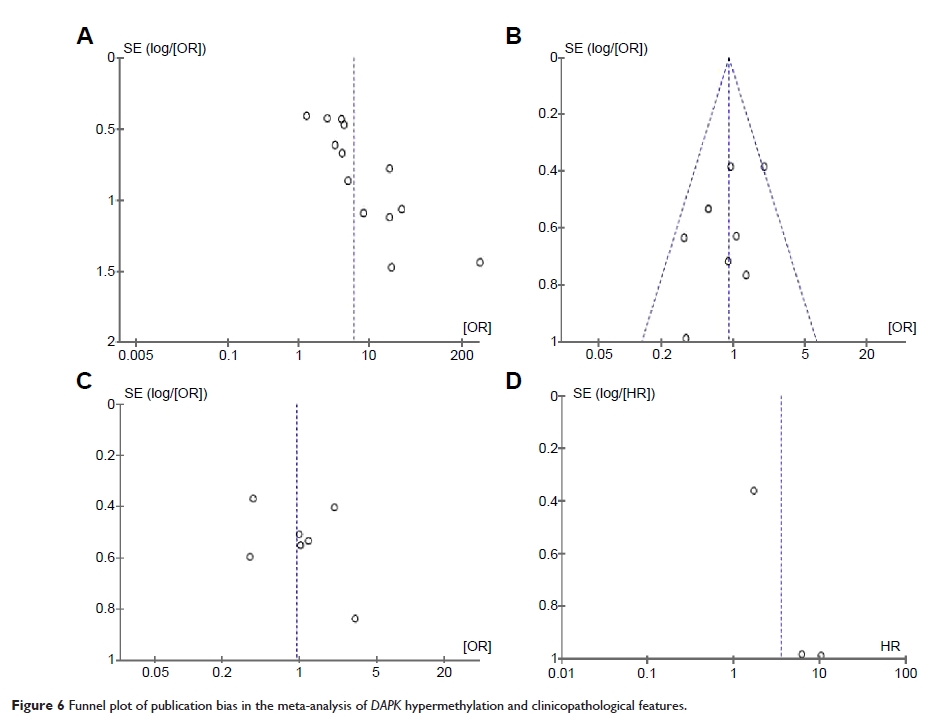
meta-analysis. We observed that the frequency of DAPK methylation was significantly higher in lung cancer than in
non-malignant lung tissues (odds ratio 6.02, 95% confidence interval
3.17–11.42, P <0.00001). The pooled results
also showed the presence of a prognostic impact of DAPK gene methylation in lung cancer patients (odds ratio 3.63, 95% confidence
interval 1.09–12.06, P =0.04). In
addition, we summarized these findings and discuss tumor suppressor function,
clinicopathological significance, and potential drug targeting
of DAPK in lung cancer.
Keywords: lung, adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, death-associated protein kinase gene, DAPK , methylation, meta-analysis
Keywords: lung, adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, death-associated protein kinase gene, DAPK , methylation, meta-analysis