108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

含有槲皮素的 RGD 修饰的纳米脂质体用于肺癌靶向治疗
Authors Zhou X, Liu H, Zhao H, Wang T
Received 28 March 2018
Accepted for publication 23 June 2018
Published 3 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5397—5405
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169555
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Purpose: The aim of this study was to prepare RGD-modified nanoliposomes containing quercetin (QCT) distearoyl-L-a-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol 2000-RGD-liposomes ([DSPE]-PEG2000-RGD-LPs/QCT) for lung cancer targeting treatment.
Methods: The physicochemical parameters of (DSPE)-PEG2000-RGD-LPs/QCT were characterized in terms of the particle size, zeta potential, morphology, entrapment efficiency, drug loading, and in vitro release behavior. In vivo, pharmacokinetics and antitumor studies of prepared formulations were also evaluated.
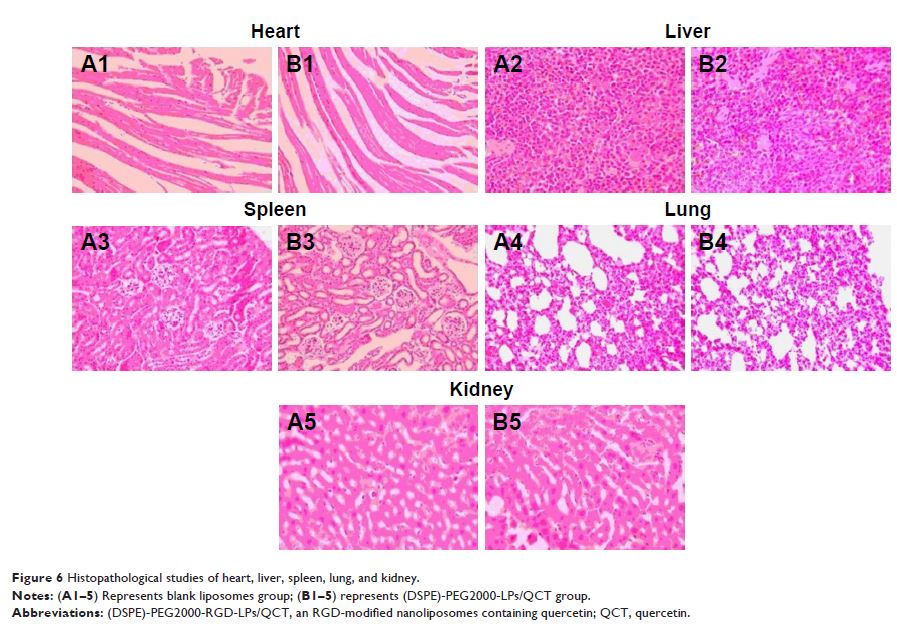
Results: In this study, QCT was found to be easily dispersed in lipid solution and entrapped by the thin-film hydration method. The encapsulation ratio and drug loading of prepared LPs were 89.2%±7.4% and 9.2%±1.3% and the mean diameter was 93.4±7.2 nm from 3 batches. The results of in vitro experiments showed that the particle size of liposomes was suitable for the fenestrated vasculatures of cancer tissues via the enhanced permeability retention effect. In vitro, a relatively slow QCT release profile was observed in (DSPE)-PEG2000-RGD-LPs, and the release mechanism fit with the Higuchi equation better. In vivo imaging results indicated that RGD-modified LPs had very good tumor targeting ability. (DSPE)-PEG2000-RGD-LPs/QCT showed a significant antitumor activity in mice with A549 tumors.
Conclusion: Through this study, it was found that the RGD-modified LPs loaded with QCT could potentially be a very promising lung-targeted preparation.
Keywords: RGD, liposomes, quercetin, pharmacokinetic, antitumor studies