108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Opioid use prior to knee arthroplasty in patients who catastrophize about their pain: preoperative data from a multisite randomized clinical trial
Authors Riddle DL, Slover JD, Ang DC, Bair MJ, Kroenke K, Perera RA, Dumenci L
Received 15 March 2018
Accepted for publication 18 May 2018
Published 21 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1549—1557
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S168251
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
Background: Opioid use rates prior to knee arthroplasty (KA) among people who catastrophize about their pain are unknown. We determined prevalence of opioid use and compared patterns of preoperative opioid use and oral morphine equivalent (OME), a measure of daily opioid dose, across varied geographic sites. We also determined which baseline variables were associated with opioid use and OME.
Patients and methods: Preoperative opioid use data described type of opioid, dosage, and frequency among 397 patients scheduled for KA. Demographic, knee-related pain, and psychological distress dimensions were examined to identify variables associated with opioid use and opioid dose (OME). Opioid use prevalence and OME were compared across the four sites. A three-level censored regression determined variables associated with opioid use and OME.
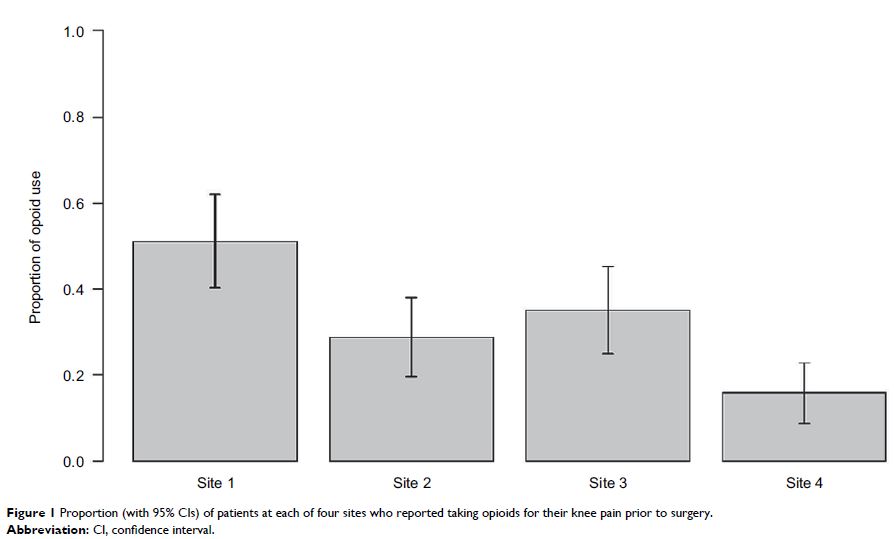
Results: The overall opioid use prevalence was 31.7% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 27.0, 36.3) and varied across sites from 15.9% (95% CI = 9.0, 22.8) to 51.2% (95% CI = 40.5, 61.9). After adjustment, patients using opioids were more likely to be younger, African American, and have higher self-efficacy and comorbidity scores (P < 0.05). The only variable independently associated with OME was lower depressive symptoms (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: People who catastrophized prior to KA did not demonstrate increased preoperative opioid use based on current evidence, but variation in the prevalence of opioid use across study sites was substantial. Variables associated with opioid use were non-modifiable demographic and comorbidity variables.
Keywords: pain, catastrophizing, opioid, knee, arthroplasty