108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA HNF1A-AS1 在中国癌症患者中的预后作用:一项综合分析
Authors Zhuang C, Zheng L, Wang P
Received 25 January 2018
Accepted for publication 27 June 2018
Published 31 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5325—5332
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S163575
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) play important roles in tumorigenesis and progression. Recent studies have demonstrated that LncRNA HNF1A antisense RNA 1 (HNF1A-AS1 ) is aberrantly expressed in several types of cancers and is associated with poor outcomes. This meta-analysis was conducted to investigate the relationship between HNF1A-AS1 expression and clinical outcomes in cancer patients.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Wan Fang databases (updated until December 31, 2017) for literature. A total of eight studies with 789 cancer patients were finally included in the present meta-analysis.
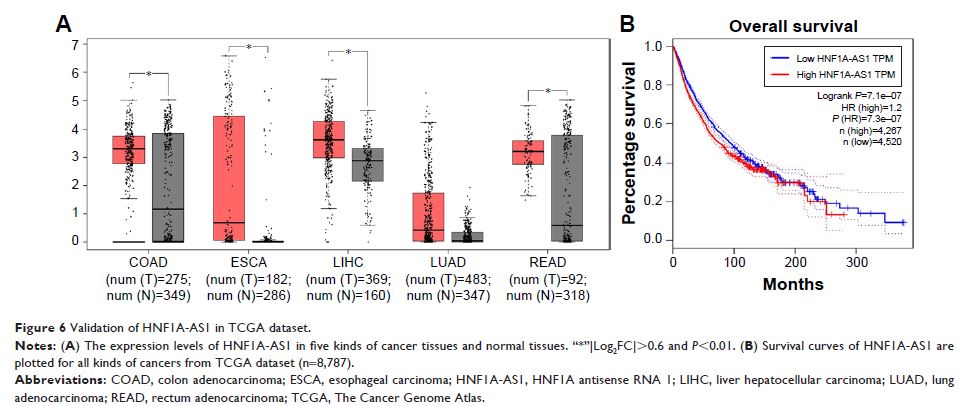
Results: The results showed that high expression of HNF1A-AS1 significantly predicted poor overall survival (HR=3.10, 95% CI: 1.58–6.11, P =0.001), which was further validated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. Moreover, high HNF1A-AS1 expression was also associated with advanced TNM stage (OR=3.32, 95% CI: 2.28–4.83, P <0.001), lymph node metastasis (OR=3.08, 95% CI: 1.95–4.85, P <0.001), and distant metastasis (OR=5.53, 95% CI: 1.94–15.77, P =0.001).
Conclusion: Our results suggested that elevated HNF1A-AS1 was associated with poor clinical outcomes and might serve as a potential prognostic biomarker of cancer.
Keywords: cancer, overall survival, TCGA, long non-coding RNA, HNF1A-AS1, meta-analysis