108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA Sox2 重叠转录物(SOX2OT)通过海绵化 microRNA 132(miR-132)促进非小细胞肺癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Zhang K, Li Y, Qu L, Ma X, Zhao H, Tang Y
Received 19 March 2018
Accepted for publication 25 May 2018
Published 30 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5269—5278
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S168654
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Sox2 overlapping transcript (SOX2OT) has been reported to be upregulated in various types of cancers, including non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the biological role and underlying mechanism of SOX2OT activity in NSCLC remain largely unknown. This study aims to investigate the function and possible molecular mechanisms of SOX2OT in NSCLC.
Materials and methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect SOX2OT expression, and cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion were measured using cell counting kit-8, wound healing, and Transwell invasion assays, respectively. Western blotting was used to determine protein expression. Starbase 2.0 and luciferase reporter assay were utilized to identify the molecular target of SOX2OT.
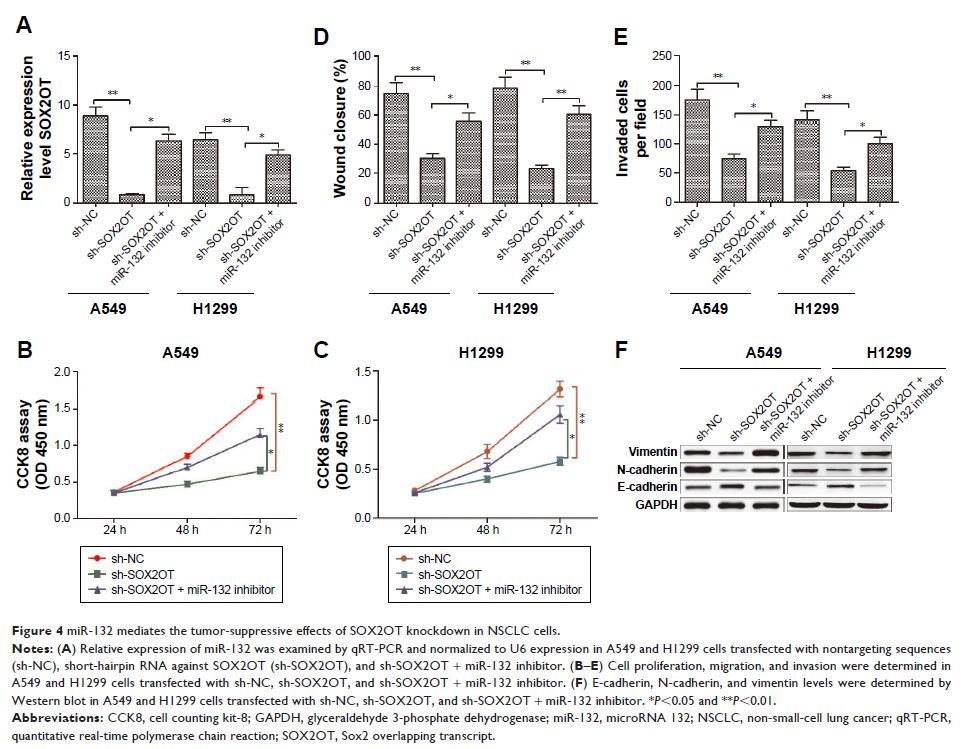
Results: Here, we discovered that SOX2OT was markedly upregulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of SOX2OT inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in NSCLC cells. Moreover, we explored the regulatory mechanism of SOX2OT and found that SOX2OT directly bound microRNA 132 (miR-132) in NSCLC cells. Importantly, miR-132 inhibition partially reversed the SOX2OT knockdown-mediated inhibitory effect on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT process. We also found that SOX2OT could regulate zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 (a target of miR-132) expression, which played crucial roles in tumor cell proliferation and invasion.
Conclusion: These findings indicated that SOX2OT was a noncoding oncogene that exerted important regulatory functions in NSCLC via sponging miR-132 and might represent a novel strategy for overcoming this disease.
Keywords: non-small-cell lung cancer, SOX2OT, miR-132, ZEB2