108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-376a 通过靶向神经毡蛋白-1NR 抑制乳腺癌细胞进展
Authors Zhang L, Chen Y, Wang H, Zheng X, Li C, Han Z
Received 7 May 2018
Accepted for publication 18 June 2018
Published 30 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5293—5302
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S173416
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
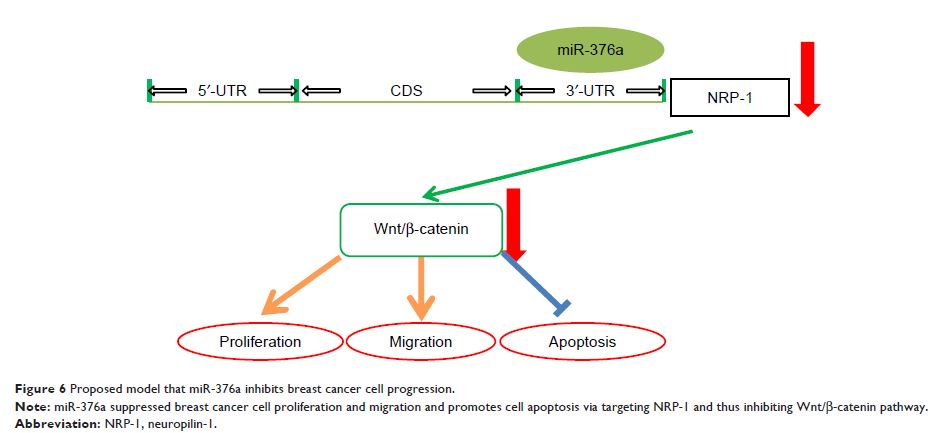
Background: The roles and related mechanism of miR-376a in breast cancer cell progression are unclear.
Methods: Kaplan-Meier plotter analysis was used to analyze the correlation between miR-376a and the overall survival (OS) of breast cancer patients. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to detect miR-376a level in breast cancer cells. Cell viability, transwell migration and invasion, and cell apoptosis were constructed to investigate the effects of miR-376a on breast cancer cells. Luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) were used to explore the targeting of miR-376a on NRP-1.
Results: miR-376a expression was positively correlated with the overall survival of breast cancer patients, and significantly decreased in breast cancer cells. Functionally, miR-376a overexpression suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and promoted cells apoptosis. Additionally, miR-376a could directly target NRP-1 and exerted its effect through NRP-1.
Conclusion: miR-376a could suppress breast cancer cell progression via directly targeting NRP-1.
Keywords: miR-376a, NRP-1, breast cancer, Wnt/β-catenin migration