108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

E2F3 促进癌症生长并且通过人黑素瘤中的拷贝数变异进行过表达
Authors Feng Z, Peng C, Li D, Zhang D, Li X, Cui F, Chen Y, He Q
Received 14 May 2018
Accepted for publication 5 July 2018
Published 30 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5303—5313
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S174103
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
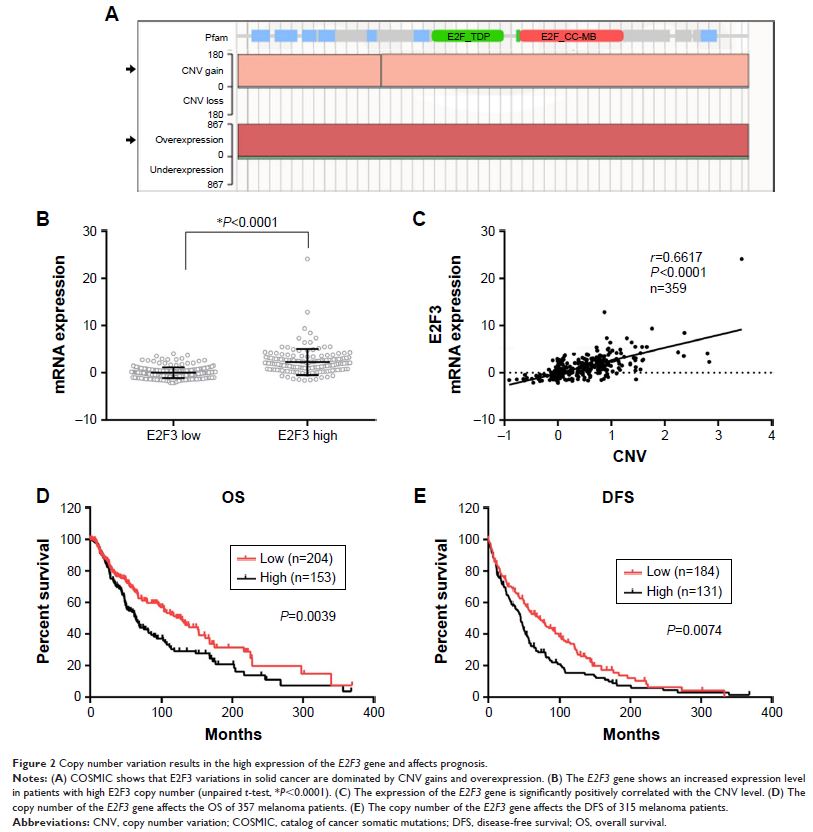
Introduction: Melanoma is a malignant tumor that seriously affects patients. The pathogenesis of malignant melanoma is complex, and the cell cycle is closely related to tumor progression. Based on the catalog of cancer somatic mutations, we found that overexpression of the E2F3 gene ranked first in percentage increase in not only melanoma but also in all human cancer tissues. However, there are few studies on the high expression of E2F3 and its carcinogenic mechanism in melanoma.
Methods and results: We found that E2F3 showed extensive copy number amplification that was positively correlated with the expression level. Patients with high copy number had a significantly poorer prognosis. We also found that E2F3 levels were significantly negatively correlated with promoter methylation. However, we showed that the E2F3 promoter region is hypomethylated, and in normal cells or tumor cells, the methylation level did not correlate with expression. Finally, we knocked down the E2F3 gene in melanoma cells by shRNA. Colony formation, anchorage-dependent growth, and EdU cell proliferation experiments showed a significant decrease in proliferation. Flow cytometry showed a significant increase in the G0/G1 ratio.
Conclusion: It can be speculated that copy number amplification and other mechanisms result in the high expression of E2F3 in melanoma, which promotes tumor progression by involving the cell cycle. E2F3 is a good target for the treatment of melanoma.
Keywords: E2F3 , melanoma, mechanism, overexpression, copy number, methylation