108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-361-5p 通过靶向 SND1 抑制胶质瘤的迁移和侵袭
Authors Liu J, Yang J, Yu L, Rao C, Wang Q, Sun CY, Shi CJ, Hua D, Zhou XX, Luo WJ, Wang R, Li WP, Yu SZ
Received 18 April 2018
Accepted for publication 1 June 2018
Published 28 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5239—5252
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S171539
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
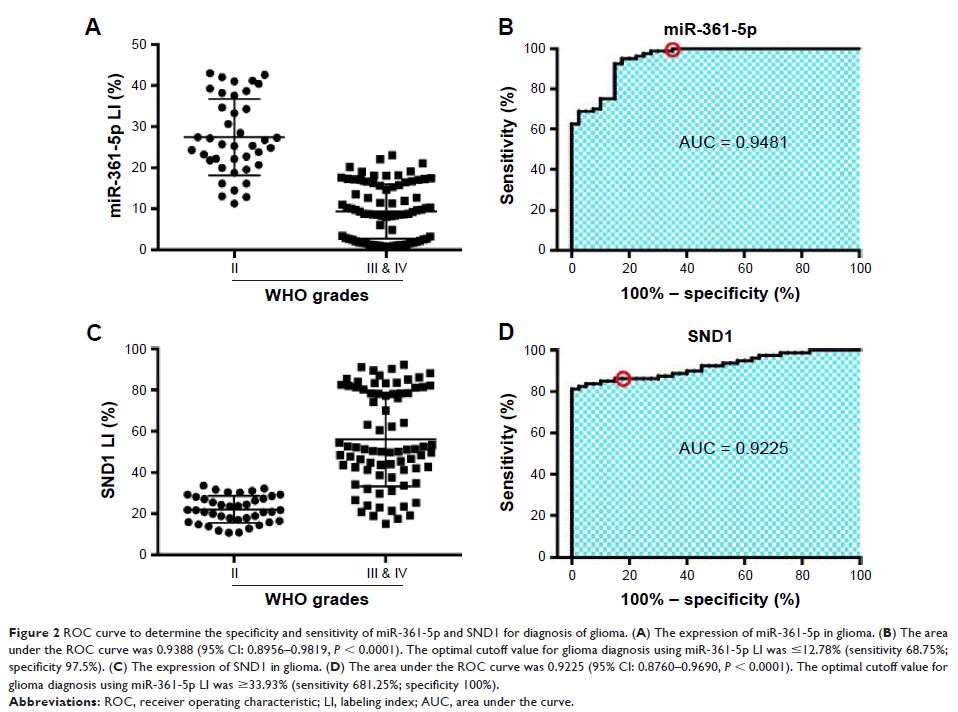
Background: Downregulation of miR-361-5p contributes to epithelial–mesenchymal transition of glioma cells. However, the relevance of miR-361-5p to migration and invasion of gliomas remains unknown.
Materials and methods: The relationship between miR-361-5p and SND1 expression was analyzed in 120 human gliomas and 8 glioma cell lines by in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to identify SND1 as a target of miR-361-5p. The mechanisms through which miR-361-5p inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion were studied by in vitro assays.
Results: miR-361-5p expression was significantly downregulated in glioma tissues and glioma cell lines, and was inversely correlated with glioma grades. However, SND1 expression was positively correlated with glioma grades and inversely correlated with miR-361-5p expression. miR-361-5p overexpression suppressed glioma cell migration and invasion through targeting SND1 and subsequently decreasing MMP-2 expression. In glioma cell lines, SND1 overexpression could partly reverse the antitumor effects of miR-361-5p.
Conclusion: The findings provide evidence that miR-361-5p directly targets SND1 to degradation and then reduces MMP-2 gene transcription, thus inhibiting glioma migration and invasion. miR-361-5p is an important tumor suppressor and a novel diagnostic biomarker of glioma, and miR-361-5p and SND1 are potential therapeutic candidates for malignant gliomas.
Keywords: miR-361-5p, glioma, SND1, migration, invasion