108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-1 mRNA 表达与乳腺超声相结合在乳腺癌患者诊断中的价值
Authors Fang J, Shao Y, Su J, Wan Y, Bao L, Wang W, Kong F
Received 17 March 2018
Accepted for publication 24 May 2018
Published 28 August 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1527—1535
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S168531
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Introduction: This study explored the value of measuring programmed death 1 (PD-1) in peripheral blood, combined with breast ultrasound using the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classification, for differentiation between benign and malignant breast tumors.
Materials and methods: We enrolled 113 patients with breast cancer and 66 patients with benign breast tumors who were admitted to Hangzhou First People’s Hospital from September 2014 to August 2017. The mRNA level of PD-1 was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
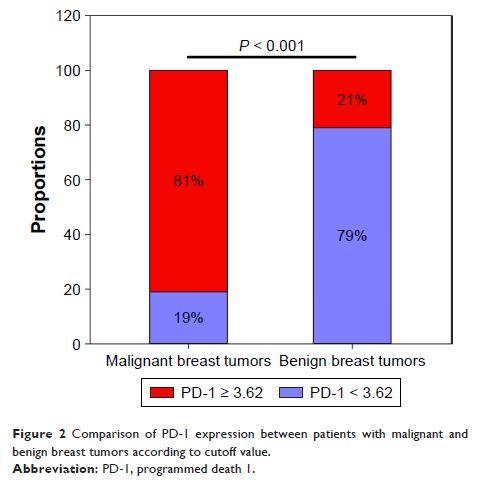
Results: The mRNA levels of PD-1 were significantly higher in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer than those in patients with benign breast tumors. The diagnostic sensitivity of PD-1 mRNA expression was 0.805, the specificity was 0.788, and the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.848 (P < 0.001); the sensitivity of breast ultrasound-based BI-RADS classification was 0.752, the specificity was 0.909, and the AUC was 0.906 (P < 0.001); and the combined sensitivity, specificity, and AUC of the two assays were 0.920, 0.879, and 0.938, respectively (P < 0.001). Progesterone receptor-positive breast cancer patients exhibited high levels of PD-1 expression (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: This study suggests that the measurement of PD-1 combined with breast ultrasound-based BI-RADS classification represents a significant improvement for breast cancer diagnosis compared with diagnoses based on either method alone.
Keywords: PD-1, breast ultrasound, diagnosis, breast cancer