108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

从猪中分离的耐甲氧西林和甲氧西林敏感的金黄色葡萄球菌的表型和分子特征: 对与家畜有关的标记物和疫苗策略的影响
Authors Guo D, Liu Y, Han C, Chen Z, Ye X
Received 9 May 2018
Accepted for publication 17 June 2018
Published 23 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1299—1307
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S173624
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Background: Routine non-therapeutic antimicrobial use and overcrowding in animal farming may facilitate the propagation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This study aimed to examine the carriage prevalence and phenotype–genotype characteristics of MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolated from pigs.
Methods: Nasal swabs were collected from 1,458 pigs in 9 pig farms and 3 slaughterhouses. All strains were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility, resistance genes, and virulence genes, and characterized by multilocus sequence typing. The correspondence analysis was conducted to explore the relationships between multiple phenotypic and molecular characteristics of S. aureus isolates.
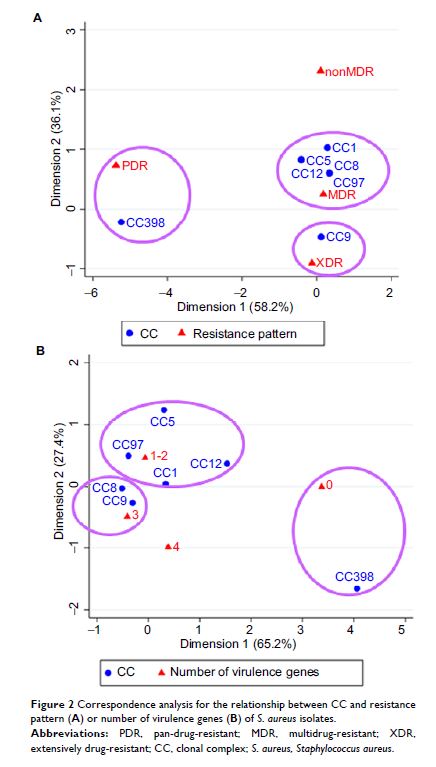
Results: In the 1,458 pigs, the carriage prevalence was 9.5% for S. aureus , 3.3% for MRSA, and 9.3% for multidrug-resistant S. aureus . Notably, 97.1% S. aureus isolates were multidrug resistant, and the predominant resistance pattern was non-susceptible to clindamycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. The predominant genotype was CC9 (ST9) for S. aureus and MRSA isolates. Importantly, all S. aureus isolates were negative for the scn gene and resistant to tetracycline. Notably, all 9 linezolid-resistant isolates were classified as multidrug resistance, including 1 expressing the cfr gene and 6 expressing the optrA gene. The correspondence analysis showed a significant relationship between clonal complexes and resistance pattern or virulence genes. For example, CC9 was associated with extensive drug-resistance and co-carrying chp , sak , and hlb , and CC1 was associated with multidrug resistance and co-carrying sak and hlb .
Conclusion: The significant correspondence relationship between multiple characteristics provides some implication for vaccine strategies and new ideas for monitoring new epidemiologic clones.
Keywords: livestock, animals, Staphylococcus aureus , antimicrobial susceptibility, multidrug resistance, molecular characterization