108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA XIST 通过靶向乳头状甲状腺癌中的 miR-141 促进增殖和侵袭
Authors Xu Y, Wang J, Wang J
Received 7 April 2018
Accepted for publication 18 May 2018
Published 21 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5035—5043
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S170439
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background: The long noncoding RNA X-inactive specific transcript (XIST ) was reported to play vital roles in tumor progression. In the present study, we determined the regulatory function of XIST in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Materials and methods: XIST expression was determined in PTC tissues and cell lines by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (qRT-PCR). Cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion were measured using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, wound-healing assay, and transwell invasion assay, respectively. Western blotting was used to determine protein expression. The downstream target miRNAs for XIST were identified by luciferase reporter assay and qRT-PCR.
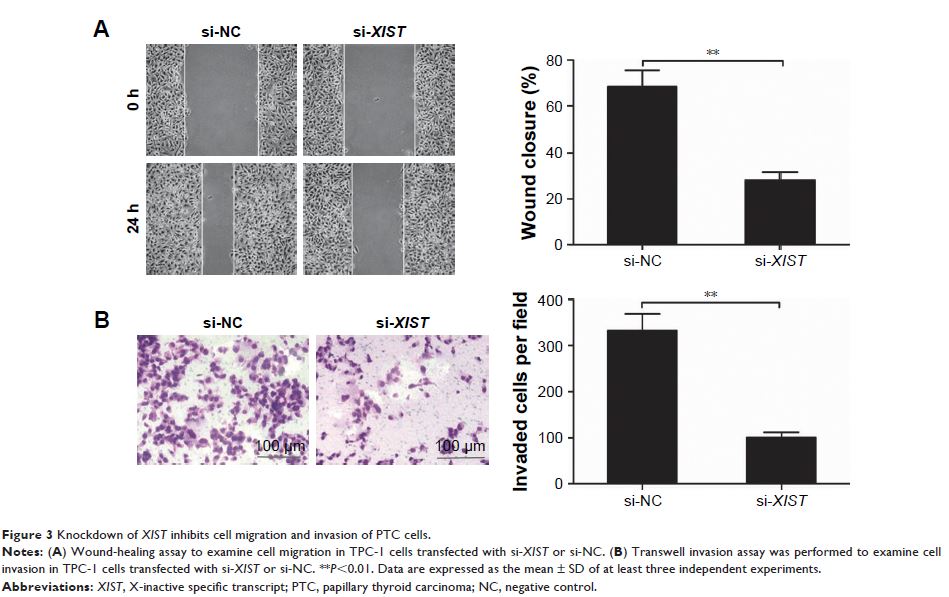
Results: Relative expression of XIST was upregulated in PTC tissues and cell lines. High XIST expression was positively correlated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis. Function assay demonstrated that knockdown of XIST significantly decreased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in PTC cells. Moreover, we showed that the effects of XIST on PTC cell progression were mediated by miR-141.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that XIST functioned as an oncogene in PTC progression by regulating miR-141, suggesting that XIST might be a promising therapeutic target for PTC treatment.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, XIST , miR-141, proliferation