108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基因工程药物 rhCNB 在胃癌细胞和肝癌细胞中诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期停滞
Authors Guo Y, Huang Y, Tian S, Xie X, Xing G, Fu J
Received 19 April 2018
Accepted for publication 21 May 2018
Published 20 August 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 2567—2575
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S171675
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Objectives: Calcineurin B (CNB) is a regulatory subunit of calcineurin, and it has antitumor activity. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of recombinant human calcineurin B (rhCNB) on the proliferation of gastric cancer cells and hepatoma cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and methods: Cell viability and cell proliferation were detected by MTT and BrdU assay. Flow cytometry, Western blot and immunohistochemistry were performed to determine rhCNB-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. The antitumor activities of rhCNB were observed in mice tumor models.
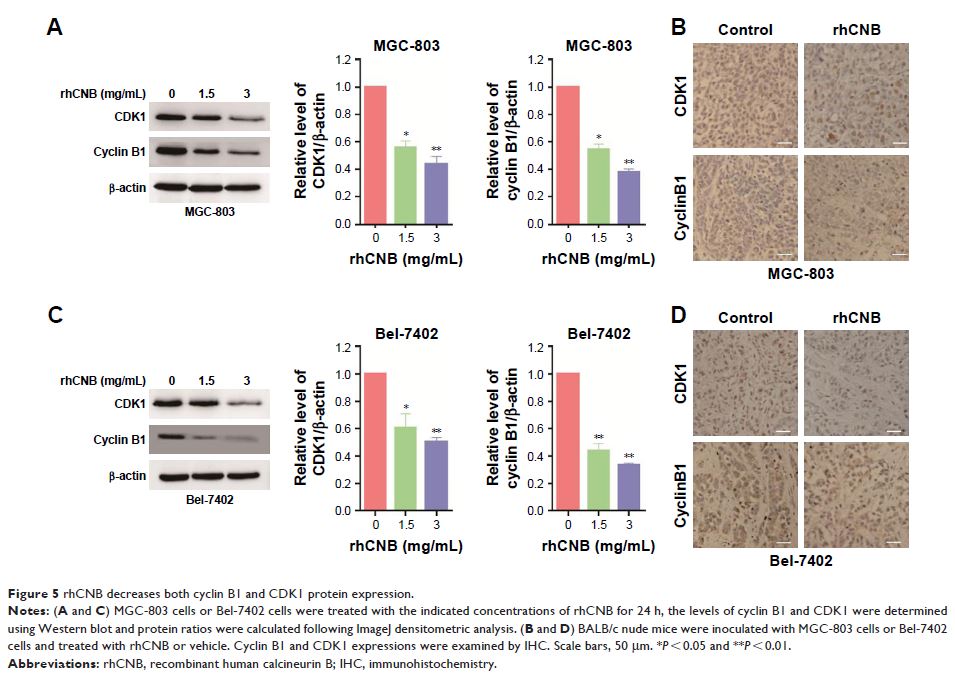
Results: We demonstrated that rhCNB inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells and hepatoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. We showed that the inhibition of cell proliferation by rhCNB is associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in both tumor cell lines. Furthermore, we indicated that rhCNB promotes p53 protein expression, a potent proapoptotic factor. Meanwhile, we also exhibited that rhCNB decreases the expression of both cyclin B1 and CDK1 proteins, two proteins associated with G2/M arrest.
Conclusion: Together, these findings suggest that rhCNB markedly inhibits tumor growth and provides guidance for its drug development.
Keywords: rhCNB, tumor cells, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, p53