108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于炎症的预后指标对鼻咽癌患者的预后价值:一项倾向值分数匹配研究
Authors Oei RW, Ye L, Kong F, Du C, Zhai R, Xu T, Shen C, Wang X, He X, Kong L, Hu C, Ying H
Received 16 April 2018
Accepted for publication 27 May 2018
Published 17 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2785—2797
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S171239
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: The aim of this article is to investigate the significance of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index (PNI), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), and their combination in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT).
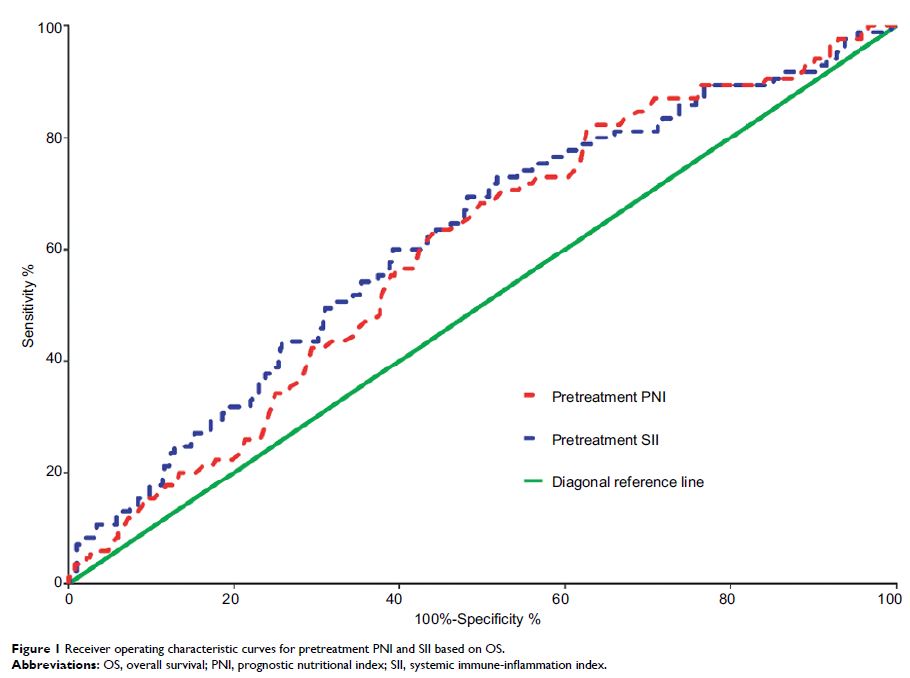
Materials and methods: A total of 585 patients were included. PNI and SII were calculated within 2 weeks prior to treatment. The optimal cutoff points were determined based on receiver operating characteristics curve analysis. The correlation between variables was analyzed. Kaplan–Meier method and Cox proportional hazards model were performed to evaluate the impact of both indices on overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS). Further propensity score matching (PSM) was carried out to minimize the effects of confounders.
Results: The optimal cutoff point of 53.0 for PNI and 527.20 for SII were selected. Pearson correlation coefficient showed an inverse correlation between PNI and SII (r = –0.232, P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that pretreatment PNI was an independent prognostic factor for OS (P = 0.047) and DMFS (P = 0.002) while pretreatment SII was an independent prognostic factor for OS (P = 0.003), PFS (P = 0.002), and DMFS (P = 0.002). After PSM, both parameters remained as independent prognosticators of survival. Additional prognostic value was observed in the combined use of PNI and SII.
Conclusion: Pretreatment PNI and SII are promising indicators of survival in NPC patients undergoing IMRT. They can be utilized to refine current TNM staging system in predicting prognosis and developing an individualized treatment in these patients.
Keywords: prognostic nutritional index, systemic immune-inflammation index, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, intensity-modulated radiotherapy, prognostic factor, survival