108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长的非编码 RNA NAP1L6 通过靶向抑制素-βA 促进肿瘤进展并预测前列腺癌的不良预后
Authors Zheng Y, Gao Y, Li X, Si S, Xu H, Qi F, Wang J, Cheng G, Hua L, Yang H
Received 24 January 2018
Accepted for publication 20 May 2018
Published 17 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4965—4977
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S163680
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background/purpose: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as key molecules in initiation and progression of prostate cancer (PCa). In this study, we aimed to explore the role of lncRNA NAP1L6 in the development and progression of PCa.
Materials and methods: We identified that lncRNA NAP1L6 was over-expressed both in PCa tissues and cell lines by gene expression array profiling. The expression level of NAP1L6 in 75 PCa tissues and adjacent tissues was detected by RT-PCR. Next, the correlations between NAP1L6 expression and clinical features of patients with PCa were analyzed by paired t-test or chi-squared test, and its association with patient prognosis was assessed by the Kaplan–Meier method. The effects of NAP1L6 on PC-3 and 22RV1 cells were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), migration, invasion, and colony formation assays. Further analysis of the results of the microarray was performed to find downstream gene of NAP1L6. Cell function experiments were performed in order to explore the relationship between NAP1L6 and Inhibin-β A (INHBA) and the specific mechanism by which INHBA affects the development of PCa.
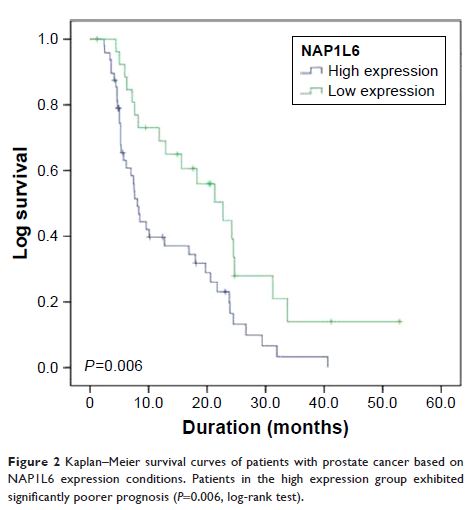
Results: Using microarray analysis, we identified 412 lncRNAs and 1245 mRNAs to be significantly differentially expressed in three PCa samples when compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues (ANTT) (fold-change ≥2.0 or ≤0.5, P <0.05, false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05). NAP1L6 expression was upregulated in PCa tissues and cell lines (both P <0.05) compared with ANTT. Besides, high expression level of NAP1L6 promotes PCa cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (all P <0.05), and is significantly associated with larger tumor diameter, distant metastasis, and shorter survival time (all P <0.05). We found that NAP1L6 promoted the expression of INHBA (P <0.05), and knockdown of NAP1L6 led to the reduction of PCa cell migration, invasion, and proliferation by regulating the expression of INHBA (all P <0.05).
Conclusion: lncRNA NR6A1 might play an oncogenic role in PCa initiation and progression by regulating the expression of INHBA, and might act as a novel prognostic biomarker for PCa treatment.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, NR6A1, INHBA, prostate cancer, prognosis