108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PRMT7 可通过与 HSPA5 和 EEF2 的相互作用促成人类非小细胞肺癌细胞的转移表型
Authors Cheng D, He Z, Zheng L, Xie D, Dong S, Zhang P
Received 1 March 2018
Accepted for publication 28 May 2018
Published 14 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4869—4876
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S166412
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) constitutes the leading cause of cancer death in humans. Previous studies revealed the essential role of the protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7 ) in promoting metastasis in breast cancer. However, its function and potential mechanism in NSCLC remain unclear.
Materials and methods: The gene expression of PRMT7 between lung cancer tissues and normal tissues was studied with online database (http://medicalgenome.kribb.re.kr/GENT/). NSCLC cell lines with specific gene overexpression were constructed with lentivirus transduction. Matrigel invasion and colony formation assays were performed to evaluate the invasion and colony formation abilities. Co-immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry analysis was performed to explore the potential interaction proteins of PRMT7 . Bioinformatic analysis was performed with Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes databases.
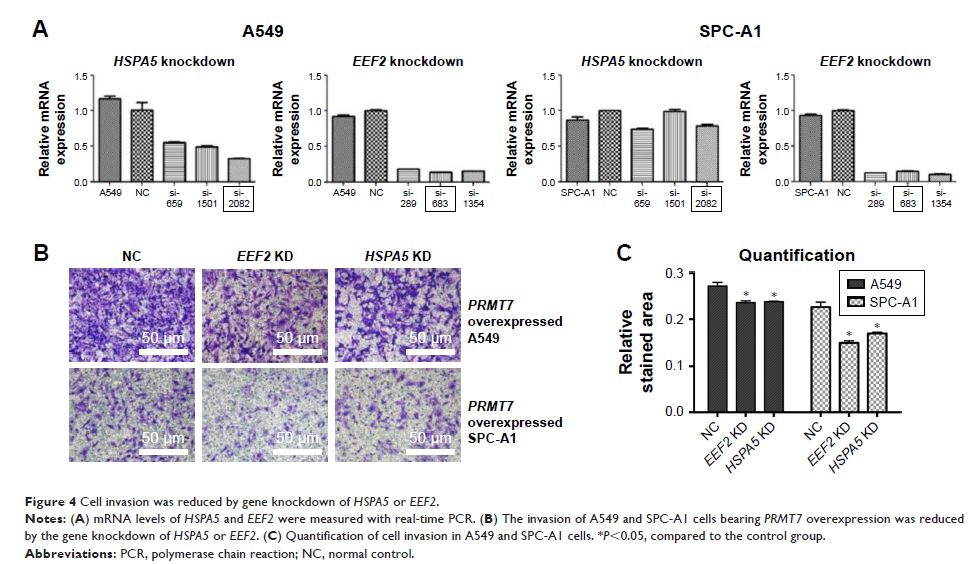
Results: Online analysis of gene expression patterns revealed the relatively high expression of PRMT7 in lung cancer tissues. PRMT7 overexpression was able to promote the invasion and colony formation of A549 and SPC-A1 cells. A total of 19 in-common proteins shared by both NSCLC cell lines were identified to be interacting with PRMT7 and found to participate in a wide variety of pathways and protein–protein interactions according to bioinformatic analysis. Among them, HSPA5 and EEF2 were further investigated for their essential roles in PRMT7 -promoted NSCLC cell invasion.
Conclusion: Our results suggested PRMT7 overexpression was able to promote metastasis in NSCLC possibly through the interaction with HSPA5 and EEF2 , which provides the potential mechanism of oncogenesis in lung cancer.
Keywords: human non-small-cell lung cancer, arginine methylation, PRMT7 , protein–protein interaction, HSPA5 , EEF