108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甲状腺乳头状癌中 AP-2α 的表达可预测肿瘤进展和预后不良
Authors Wu HR, Zhang J
Received 12 March 2018
Accepted for publication 30 May 2018
Published 13 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2615—2625
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167874
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Background: The activator protein (AP)-2α is involved in a wide variety of
biologic processes in tumor. However, little is known about the role of AP-2α
in human papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Methods: The immunohistochemical method was used to detect AP-2α expression
in 63 PTC cases. Western blotting was carried out to assess the change in
expression of certain proteins. The bioinformatics analysis of 496 PTC samples
comes from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The Gene Set Enrichment
Analysis (GSEA) was performed using TCGA data set. Cell transfection was used
to induce related protein expression or to repress it by RNA interference
procedures.
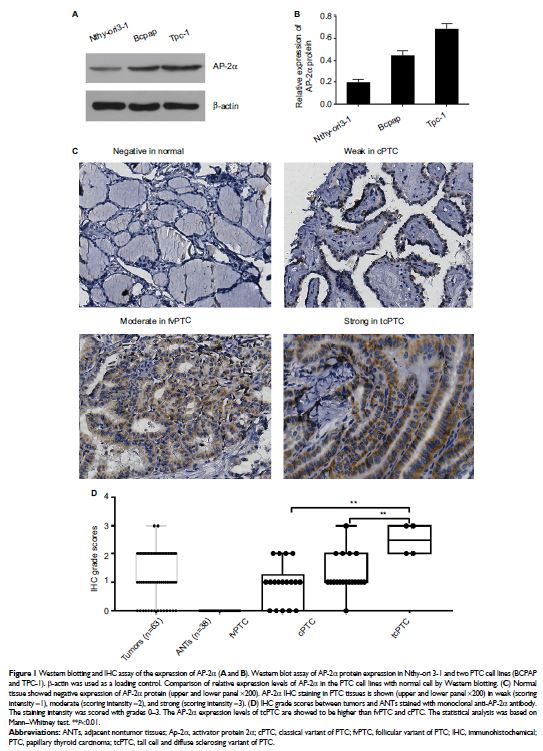
Results: Our results demonstrated that AP-2α expression was higher in tumor
tissues than the corresponding adjacent nontumor tissues, the positive
substances of AP-2α were observed mainly in the cytoplasm of PTC, and AP-2α was
positively correlated with histologic type (P =0.026) of PTC
patients. The high expression of AP-2α mRNA was associated significantly with
tumor stages (P =0.011), histologic type (P =0.019), and independently
predicted shorter overall survival (P =0.005) based on
TCGA analysis. Patients with high AP-2α mRNA expression have shorter overall
survival compared to those with low AP-2α mRNA expression, particularly in
advanced tumor stages (III and IV) of PTC patients (P =0.011).
Multivariate analysis suggested that AP-2α mRNA expression might be an
independent prognostic indicator for the survival of patients with PTC (P =0.037). Moreover, the
association between enhanced AP-2α expression and two pathways (notch signaling
and focal adhesion) was revealed by GSEA, and then confirmed by cellular
experiments.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings suggest that AP-2α may be a potential
prognostic molecular marker and therapeutic target for PTC patients.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, AP-2α, prognosis, overall survival,
notch signalling