109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
在小鼠脓毒症预防和治疗中作为抗炎剂的一类新的姜黄素类似物的合成和生物评价
Authors Zhao C, Zhang Y, Zou P, Wang J, He W, Shi D, Li H, Liang G, Yang S
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 1663—1678
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S75862
Received 15 October 2014, Accepted 20 November 2014, Published 18 March 2015
Abstract: A novel class of asymmetric mono-carbonyl analogs of curcumin (AMACs)
were synthesized and screened for anti-inflammatory activity. These analogs are
chemically stable as characterized by UV absorption spectra. In vitro,
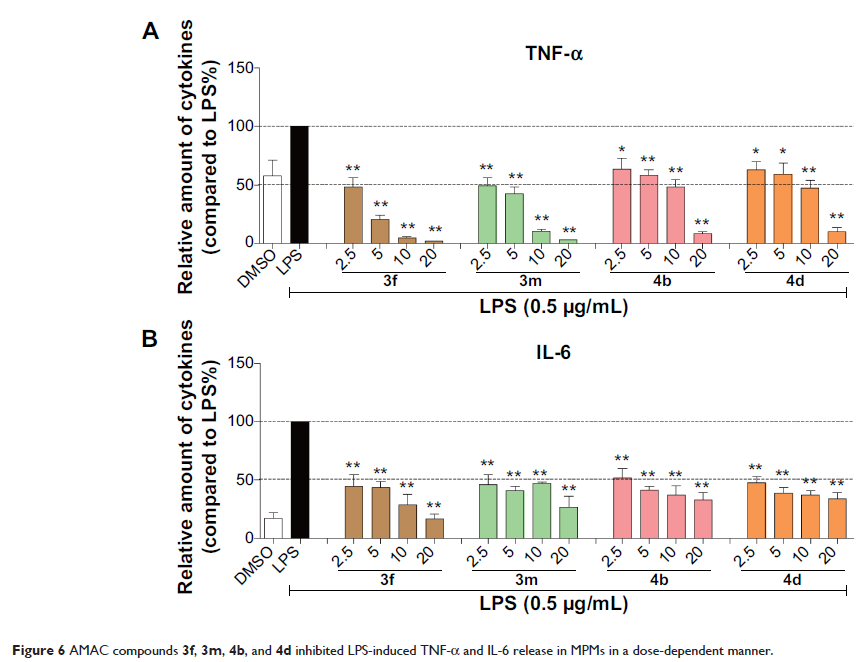
compounds 3f, 3m, 4b, and 4d markedly inhibited
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor
necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values in low micromolar range. In vivo, compound 3f demonstrated potent
preventive and therapeutic effects on LPS-induced sepsis in mouse model.
Compound 3f downregulated the
phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 MAPK and
suppressed IκBα degradation, which suggests that the possible anti-inflammatory
mechanism of compound 3f may be
through downregulating nuclear factor kappa binding (NF-κB) and ERK pathways.
Also, we solved the crystal structure of compound 3e to confirm the asymmetrical
structure. The quantitative structure–activity relationship analysis reveals
that the electron-withdrawing substituents on aromatic ring of lead structures
could improve activity. These active AMACs represent a new class of
anti-inflammatory agents with improved stability, bioavailability, and potency
compared to curcumin. Our results suggest that 3f may be further developed as a potential agent for prevention and treatment of
sepsis or other inflammation-related diseases.
Keywords: asymmetric mono-carbonyl analogs of curcumin (AMACs), stability, anti-inflammatory property, sepsis, QSAR
Keywords: asymmetric mono-carbonyl analogs of curcumin (AMACs), stability, anti-inflammatory property, sepsis, QSAR