108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

药物对 PD-1/PD-L1 阻断的反应:基于生物标志物
Authors Chen Q, Li T, Yue W
Received 15 March 2018
Accepted for publication 12 May 2018
Published 8 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4673—4683
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S168313
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
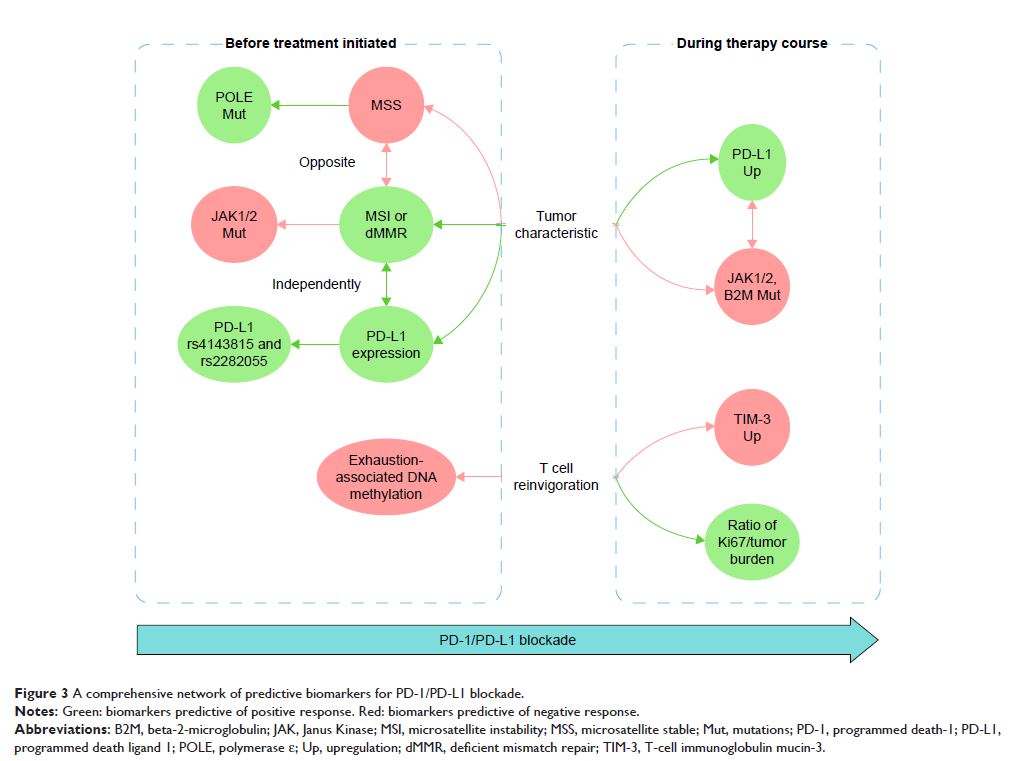
Abstract: In recent years, immunotherapies targeting programmed death-1
(PD-1)/programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) have provided great hopes for patients
with cancer. A successful anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy includes not only the
elimination of immunosuppressive tumor cells but also the rejuvenation of
exhausted T cells. Nevertheless, the efficacy of therapy is still low, so that
biomarker-driven therapy has attracted more and more attention to identify
patients who are likely to benefit from therapy and to reduce unnecessary
disease progression. While many studies have focused on characteristics of
tumor biopsies, biomarkers linked to T cell exhaustion and rejuvenation have
just become new hot spots in drug response studies. However, no biomarker is
perfect in drug response prediction currently, so there is an urgent need for
other biomarkers to compensate for the deficiency. In this review, we summarize
some approved and candidate biomarkers predictive of drug response before and
during PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, including those characterizing responsive or
suppressive tumor cells and those evaluating the T cell rejuvenation. Overall,
we set up a comprehensive network of biomarkers of tumor characteristics and T
cell rejuvenation, predicting drug response before and during anti-PD-1/PD-L1
therapies.
Keywords: PD-1, PD-L1, biomarker, network, tumor, T cell rejuvenation