108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于预测免疫检查点抑制剂反应的生物标志物的当前前景和未来方向
Authors Zhu Y, Zhao F, Li Z, Yu J
Received 6 March 2018
Accepted for publication 21 May 2018
Published 7 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2475—2488
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167400
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Abstract: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), represented by anti-CTLA-4 or
anti-PD-1/ anti-PD-L1 pathway antibodies, have led to a revolution in cancer
treatment modalities. ICIs have unique clinical benefits, such as effectiveness
against a broad range of tumor types, strong overall impact on survival, and
persistent responses after the cessation of therapy. However, only a subset of
patients responds to these therapies, and a small proportion of patients even
experience rapid progression or an increased risk of death. Therefore, it is
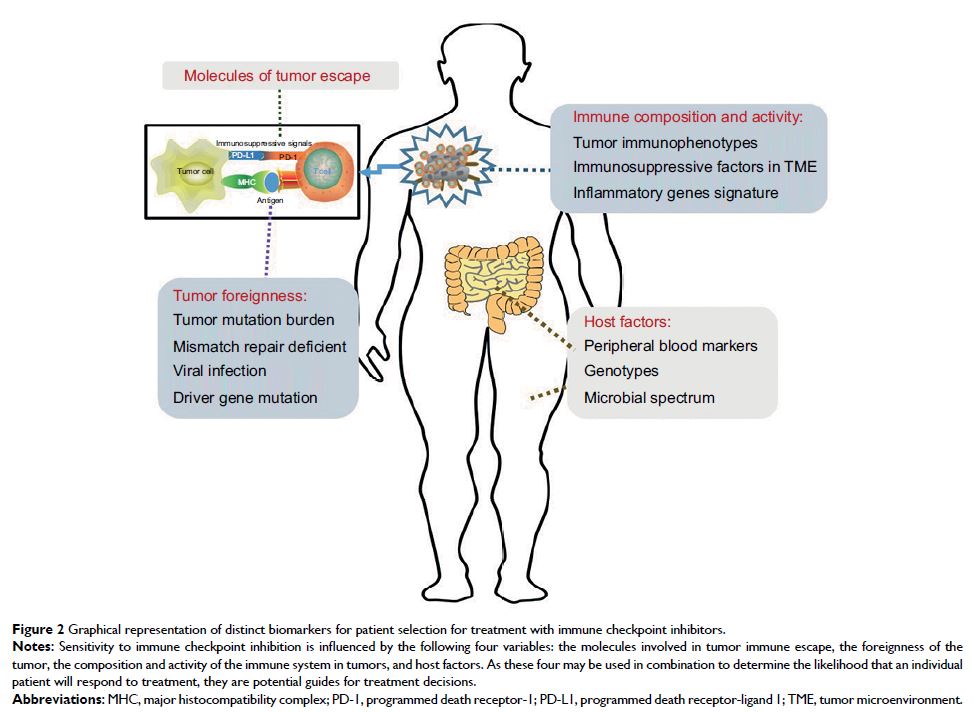
imperative to optimize patient selection for treatment. This review focuses on
the mechanisms of tumor escape from immune surveillance, the composition and
activity of a preexisting immune infiltrate, the degree of tumor foreignness
(as reflected by the mutational burden, expression of viral genes, and driver
gene mutations), and host factors (including peripheral blood biomarkers,
genetic polymorphisms, and gut microbiome) to summarize current evidence on the
biomarkers of responses to ICIs and explore the future prospects in this field.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitor, programmed death-1, programmed death
ligand-1, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4, biomarker, efficacy