108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长的非编码 RNA MAP3K1-2 促进胃癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Wu L, Yin JH, Guan YY, Liu HL, Shen HL, Wang XJ, Han BH, Zhou MW, Gu XD
Received 21 March 2018
Accepted for publication 12 June 2018
Published 7 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4631—4639
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S168819
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in several
human cancers. The expression profile and underlying mechanism of the lncRNA
MAP3K1-2 in gastric cancer (GC) are poorly understood.
Methods: Sixty-one patients with GC were recruited from Shanghai Baoshan
Luo Dian Hospital (Shanghai, China). Tumor tissues and paired normal tissues (5
cm adjacent to the tumor) were obtained. Expression of lncRNA MAP3K1-2 in GC
cell lines was examined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Protein expression was detected using Western blot. Cell cycle analysis was assessed
using flow cytometry. Cell proliferation was assessed using soft agar assays,
and cell invasion was assessed using Transwell assays.
Results: The expression level of lncRNA MAP3K1-2 was upregulated in GC
cells and markedly higher in poorly differentiated cell lines. Silencing
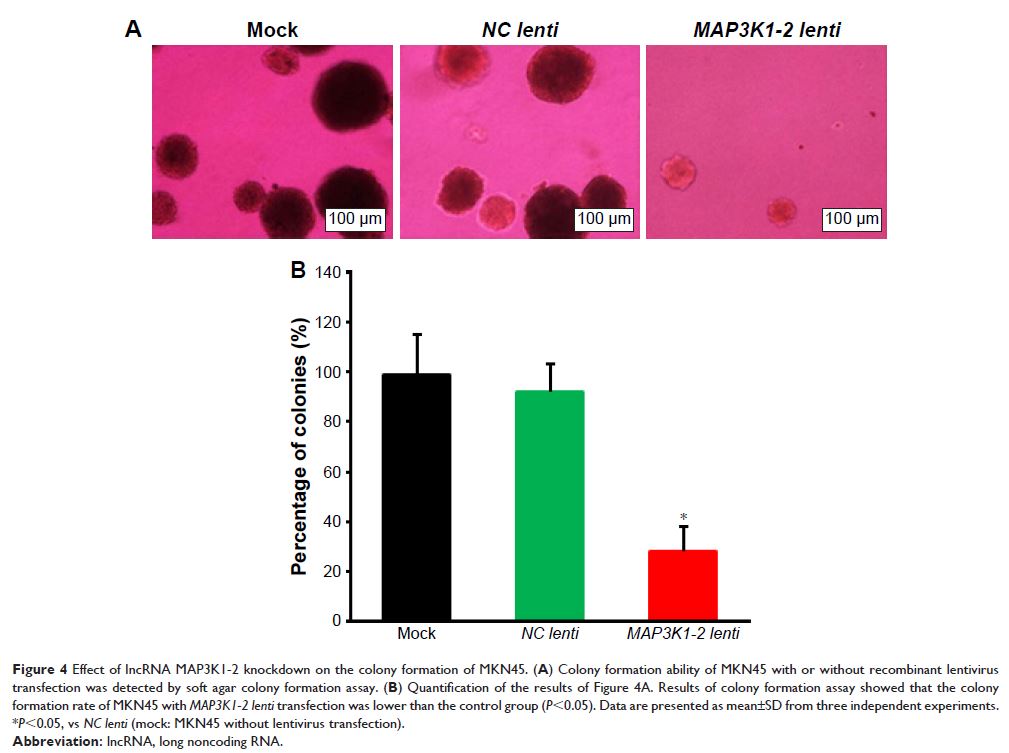
treatment of lncRNA MAP3K1-2 significantly inhibited cell proliferation and
invasion in GC. In addition, knockdown of lncRNA MAP3K1-2 significantly
inhibited the function of important genes in the MAPK signaling pathway. Higher
expression of lncRNA MAP3K1-2 was often associated with poorer prognosis in
patients with GC.
Conclusions: lncRNA MAP3K1-2 is a critical effector in GC tumorigenesis and
progression, representing novel therapeutic targets. High lncRNA MAP3K1-2
expression may serve as a novel independent prognostic marker for predicting
the outcome of GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, long noncoding RNA, MAP3K1-2