108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用基于 18F-氟脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描成像对中国实验参与者与帕金森病有关的糖代谢异常进行验证
Authors Jin R, Ge J, Wu P, Lu J, Zhang H, Wang J, Wu J, Han X, Zhang W, Zuo C
Received 12 March 2018
Accepted for publication 9 May 2018
Published 6 August 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1981—1989
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S167548
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Purpose: We previously identified disease-related cerebral metabolic
characteristics associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD) in the Chinese
population using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography
(PET)/computed tomography (CT) imaging. The present study aims to assess data
reproducibility and robustness of the metabolic activity characteristics across
independent cohorts.
Patients and
methods: Forty-eight patients with PD and 48
healthy controls from Chongqing district, in addition to 33 patients with PD
and 33 healthy controls from Shanghai district were recruited. Each subject
underwent brain 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in a resting state. Based on the brain
images, differences between the groups and PD-related cerebral metabolic
activities were graphically and quantitatively evaluated.
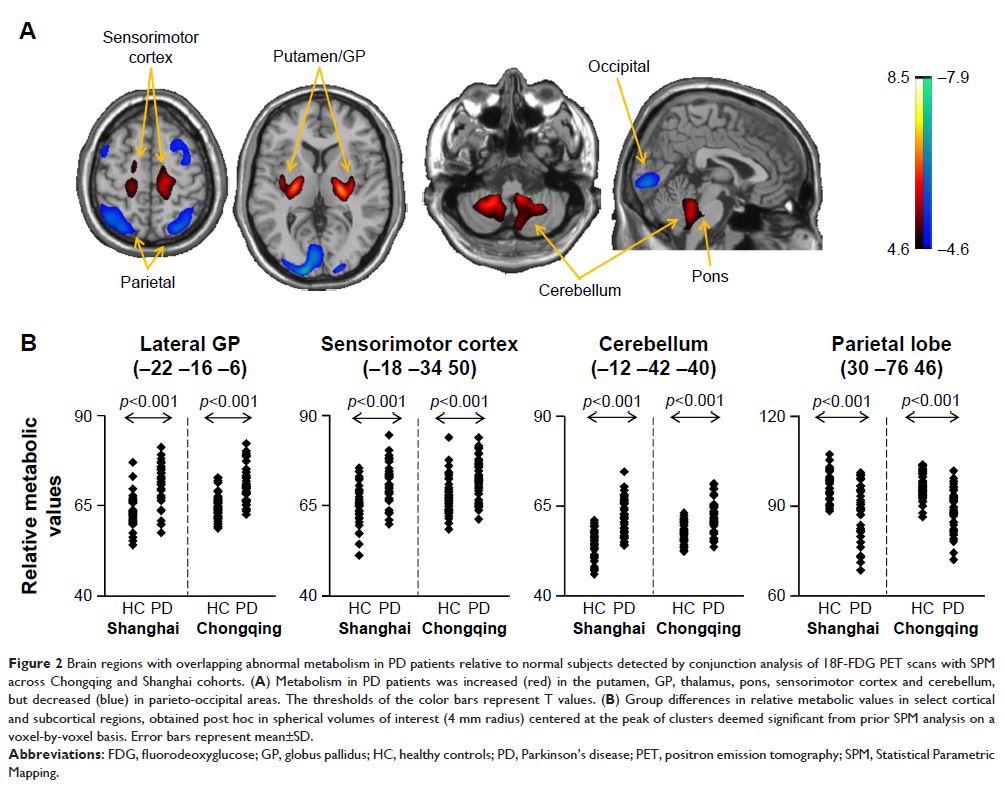
Results: Both PD patient cohorts exhibited analogous cerebral patterns
characterized by metabolic increase in the putamen, globus pallidus, thalamus,
pons, sensorimotor cortex and cerebellum, along with metabolic decrease in
parieto-occipital areas. Additionally, the metabolic pattern was highly
indicative of the disease, with a significant elevation in PD patients compared
with healthy controls (p <0.001) in both
the derivation (Shanghai) and validation (Chongqing) cohorts.
Conclusion: This dual-center study demonstrated the high comparability and
reproducibility of PD-related cerebral metabolic activity patterns across
independent Chinese cohorts and may serve as an objective diagnostic marker for
the disease.
Keywords: movement disorders, parkinsonism, disease diagnosis, positron
emission tomography, neuroimaging marker, Parkinson’s disease