108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

缺氧调节的 lncRNA CRPAT4 可通过调节透明细胞肾细胞癌中的 AVL9 促进细胞迁移
Authors Zhang W, Wang J, Chai R, Zhong G, Zhang C, Cao W, Yan L, Zhang X, Xu Z
Received 24 March 2018
Accepted for publication 23 May 2018
Published 3 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4537—4545
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169155
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Introduction: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are proven to be key regulators in
cancer biology. Our screening effort for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
(ccRCC) prognosis-associated lncRNAs identified a novel lncRNA, ccRCC
prognosis-associated transcript 4 (CRPAT4), as one of the top candidates that
was previously uncharacterized. The aim of this study was to verify the
clinical significance of CRPAT4 in ccRCC patients and to explore its biological
role as well as the underlying mechanisms, in ccRCC cell lines.
Materials and
methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase
chain reaction (PCR) was performed to demonstrate that CRPAT4 was
differentially expressed between ccRCC and the normal controls and that high
CRPAT4 expression significantly associated with advanced Fuhrman nuclear
grades.
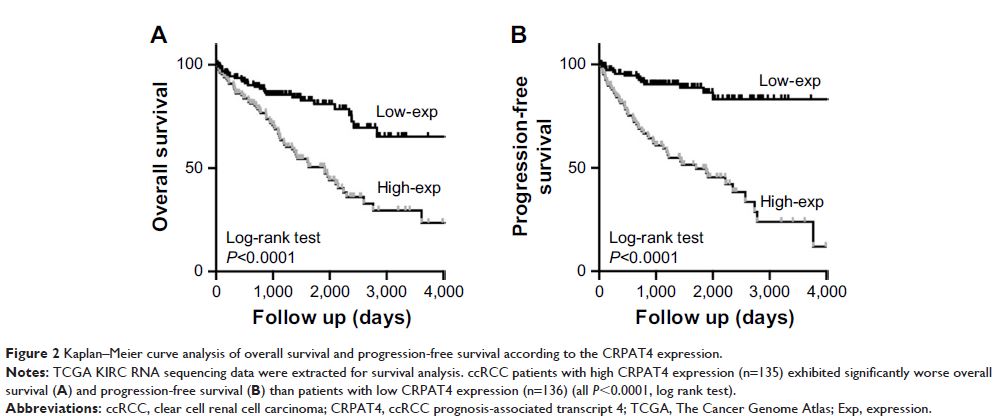
Results: Kaplan–Meier survival analysis with The Cancer Genome Atlas KIRC
RNA sequencing data indicated that high CRPAT4 expression was significantly
associated with poor overall survival and progression-free survival. Functional
studies indicated that CRPAT4 was an HIF-1α regulated gene, and CRPAT4
knockdown significantly inhibited cell migration and proliferation in the
absence of HIF-1α. In addition, a mechanistic study revealed that CRPAT4 could
regulate the expression of the migration-associated protein AVL9.
Conclusion: Collectively, our study first identified CRPAT4 as a
hypoxia-regulated lncRNA, acting as an oncogene in ccRCC progression via
regulating AVL9 protein, thus expanding our knowledge on the hypoxia pathway in
ccRCC biology from a noncoding perspective. Moreover, CRPAT4 has the potential
to be a prognostic marker in ccRCC patients.
Keywords: CRPAT4, AVL9, hypoxia, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, migration