108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

评估皮肤接触金属纳米颗粒的免疫反应和细胞毒性
Authors Wang M, Lai X, Shao L, Li L
Received 11 April 2018
Accepted for publication 5 June 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4445—4459
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S170745
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Mohankandhasamy Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
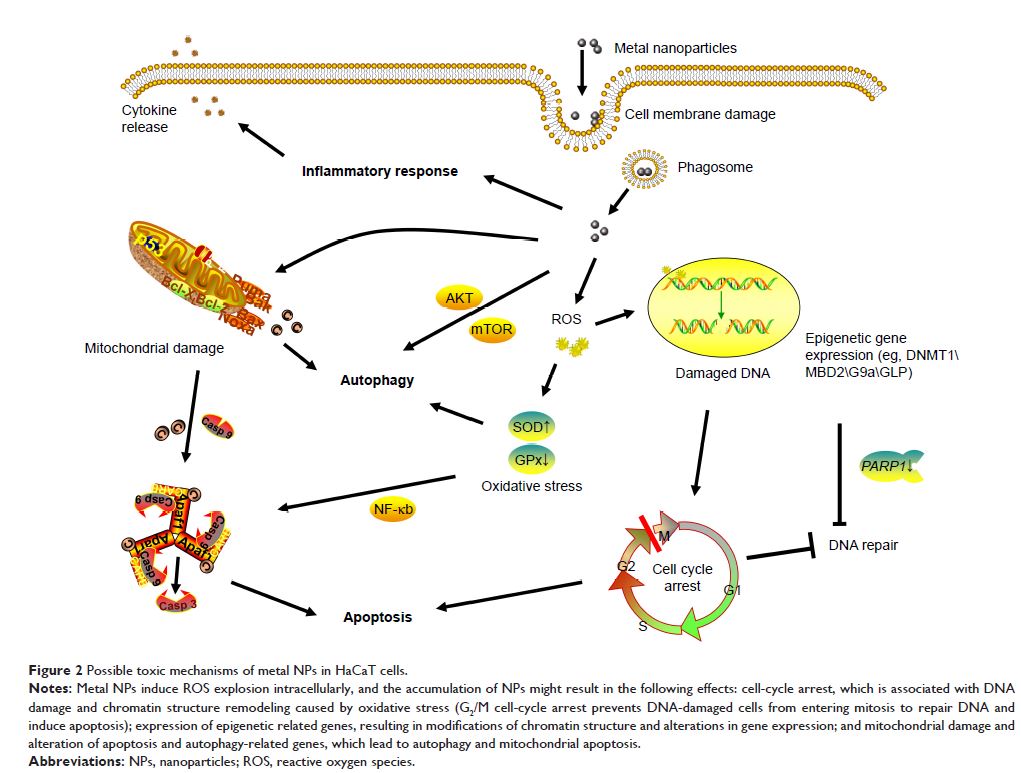
Abstract: Nanotechnology is an interdisciplinary science that has developed
rapidly in recent years. Metallic nanoparticles (NPs) are increasingly utilized
in dermatology and cosmetology, because of their unique properties. However,
skin exposure to NPs raises concerns regarding their transdermal toxicity. The
tight junctions of epithelial cells form the skin barrier, which protects the
host against external substances. Recent studies have found that NPs can pass
through the skin barrier into deeper layers, indicating that skin exposure is a
means for NPs to enter the body. The distribution and interaction of NPs with
skin cells may cause toxic side effects. In this review, possible penetration
pathways and related toxicity mechanisms are discussed. The limitations of
current experimental methods on the penetration and toxic effects of metallic
NPs are also described. This review contributes to a better understanding of
the risks of topically applied metallic NPs and provides a foundation for
future studies.
Keywords: metallic nanoparticles, transdermal penetration, toxicity