108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对与子宫内膜癌转移调控过程相关的 4 种 miRNA 的生物信息学分析
Authors Zhu L, Shu Z, Shun X
Received 19 March 2018
Accepted for publication 21 May 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2337—2346
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S168594
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of
different miRNAs in nonmetastatic and metastatic endometrial cancer Existing
evidence indicates that there are many factors affecting the metastasis of
endometrial cancer, and miRNAs play an unique role in many processes of
endometiral cancer.
Materials and
methods: miRNA sequences were downloaded from
The Cancer Genome Atlas Project database, and Bioinformatics technique was used
to deal with those data.
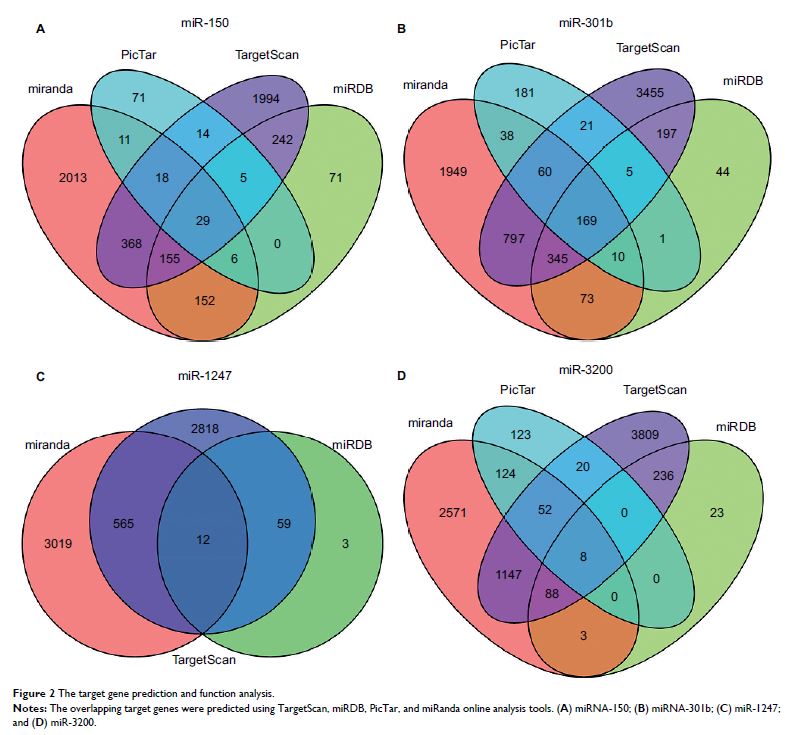
Results: We elucidated the relation between differentially expressed miRNAs
and clinical information for a total of 260 tumor tissues and 22 tumor tissues
that had metastasized. We used the threshold of P <0.05| log 2 FC |
>1.2 to identify potential miRNAs. Four differentially expressed miRNAs were
identified in nonmetastatic and metastatic endometrial cancers. Further
differential analysis of metastatic tissue revealed that miR-1247 is associated
with metastasis of endometrial cancer to the lung, and miR-3200 is associated
with the clinical stage of endometrial cancer. A functional enrichment analysis
showed that the four miRNAs may be involved in multiple pathways of cancer,
including the Wnt, NOTCH, and TGF-β signaling pathways and signaling pathways
regulating pluripotency of stem cells. Protein–protein interaction analysis
showed that PAK6 , SNAP25 , MAN1A1 , MYB , ZBTB4 , UST , ALDH1A3 , and NRP2 are hub genes of
relevant miRNAs in endometrial cancers.
Conclusion: The current study indicates that these four miRNAs may be related
to molecular markers of metastasis of endometrial cancer.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, bioinformatics, miR-1247, protein analysis