108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LRH-1 部分通过诱导 c-myc 和周期蛋白 E1,以及抑制 p21 来驱动肝细胞癌
Authors Xiao L, Wang Y, Liang W, Liu L, Pan N, Deng H, Li L, Zou C, Chan FL, Zhou Y
Received 17 January 2018
Accepted for publication 1 June 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2389—2400
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S162887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: To explore potential therapeutic target is one of the areas of
great interest in both clinical and basic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
studies. Nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1, NR5A2 ) is proved to play a
positive role in several cancers including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and
intestinal cancer in recent years. However, the exact role of LRH-1 in the
development and progression of HCC is not fully elucidated.
Methods: The LRH-1 expression level in HCC clinical samples was examined by
immunohistochemistry (IHC). Stable LRH-1-suppressed HepG2 clones (HepG2LRH-1/-) were generated by transcription activator-like effector nucleases
(TALENs) and both in vitro and in vivo experiments were conducted.
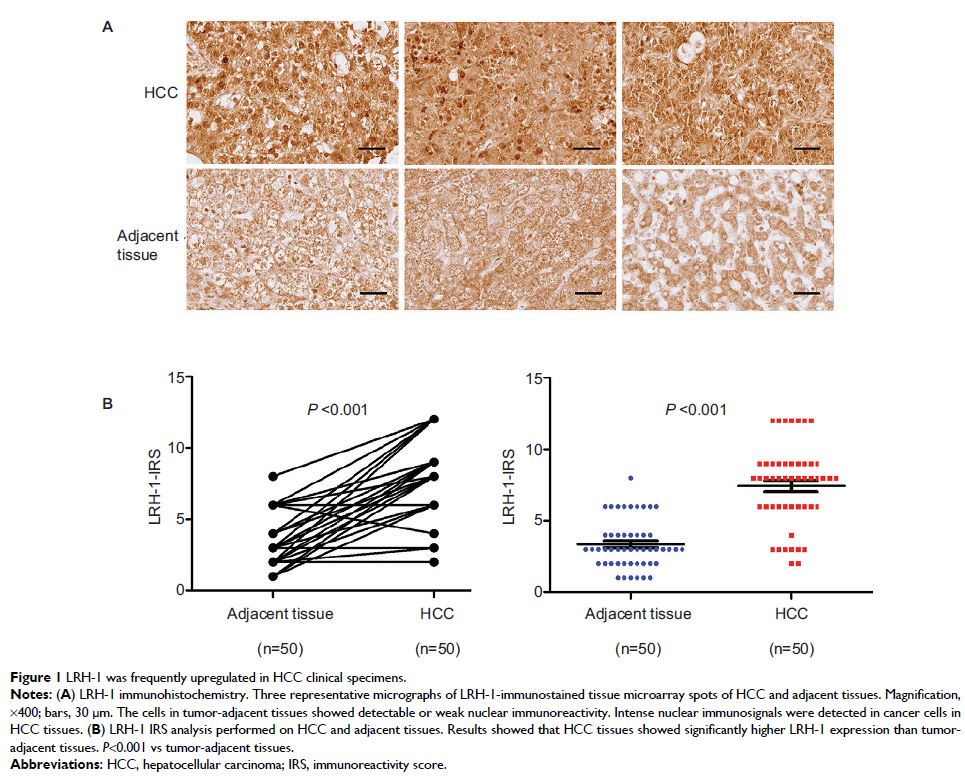
Results: We confirmed that LRH-1 showed an increased expression pattern in
HCC clinical samples. Our in vitro and in vivo results indicated that
suppression of LRH-1 in HepG2 significantly attenuated its proliferation rate
and tumorigenic capacity. Gene expression microarray analysis indicated that
LRH-1mostly regulated gene expression involved in cell cycle. In addition, our
gain-of-function experiments indicated that ectopic expression of LRH-1
dramatically induced the mRNA and protein levels of c-myc and cyclin E1, while
attenuating the expression of p21.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that LRH-1 might be a potential therapeutic
target for clinical HCC treatment.
Keywords: LRH-1, HCC, c-myc, p21, cyclin E1