108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

扎鲁司特与伪金丝桃素联合可减弱实验小鼠的脊髓损伤和运动功能
Authors Chen XG, Hua F, Wang SG, Xu YY, Yue HT, Sun J
Received 22 October 2017
Accepted for publication 22 March 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 2389—2402
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S154814
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Biosynthesis of leukotriene (LT) by arachidonic acid involves
5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) as an important precursor. Here, we evaluated the role of
pseudohypericin (PHP) for its postulated 5-LO inhibitory activity along with a
Cys-LT receptor antagonist zafirlukast (ZFL) against inflammatory response and
tissue injury in mice.
Materials and
methods: The spinal injury was induced by
two-level laminectomy of T6 and T7 vertebrae. The inflammation was assessed by
histology, inflammatory mediators by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,
apoptosis by Annexin-V, FAS staining, terminal
deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated UTP end labeling (TUNEL) assay and expression
of Bax and Bcl-2 by Western blot. Effect on motor recovery of hind limbs was
evaluated for 10 days postinjury.
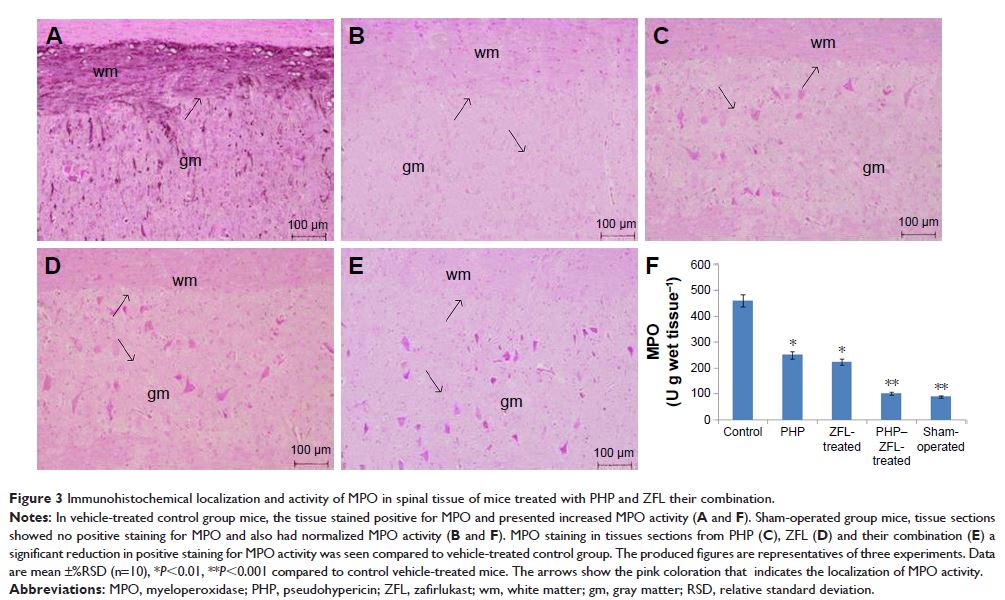
Results: The spinal injury resulted in tissue damage, apoptosis, edema,
infiltration of neutrophils with increased expression of tumor necrosis
factor-α (TNF-α) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). The spinal tissue showed
elevated levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and LTB4 and increased
phosphorylation of injured extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2).
The PHP, ZFL and combination decreased inflammation, tissue injury and
infiltration of neutrophils. Treatment also decreased the levels of PGE2,
phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (pERK 1/2), LT,
TNF-α and COX-2 with a marked reduction in apoptosis and improved the motor
function.
Conclusion: The present study confirmed 5-LO antagonist activity of PHP and
established its neuroprotective role along with ZFL.
Keywords: pseudohypericin, zafirlukast, 5-lipoxygenase, Cys-LT, mice