108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对侧单关节炎通过上调诱导型一氧化氮合酶加剧慢性压迫性损伤引起的疼痛超敏反应
Authors Zhao H, Liu S, Wang C, Wang Q, Liu W, Gong M
Received 1 March 2018
Accepted for publication 4 May 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1433—1443
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S166994
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael E Schatman
Introduction: High comorbidity of osteoarthritis (OA) and neuropathic pain has
been reported in aged patients. Evidence shows that central sensitization of
pain processing occurs in late-phase OA and may facilitate the development of
neuropathic pain. Few studies reveal whether acute monoarthritis (MA)
aggravates neuropathic pain on the opposite side of the body from the
injury.
Methods: To address whether neuropathic pain is affected by contralateral
MA through distinct inflammatory pathway, MA was induced by intra-articular
injection of complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) into the right tibiotarsal joint,
and neuropathic pain was established by chronic constriction injury (CCI) of
the left sciatic nerve.
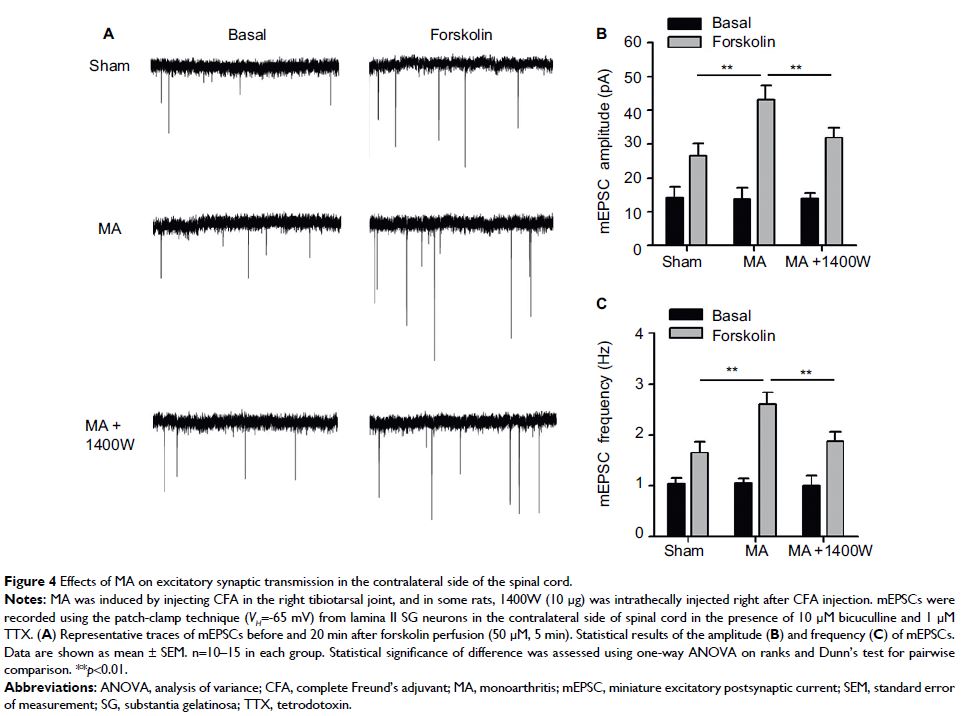
Results: We observed that MA aggravated mechanical allodynia and thermal
hyperalgesia in CCI rats. Furthermore, MA affected the other side of the spinal
cord in multiple aspects, including the upregulation of iNOS mRNA and the
enhancement of forskolin-induced facilitation of excitatory synaptic
transmission in the spinal cord dorsal horn substantia gelatinosa
neurons.
Discussion: Interestingly, intrathecal injection of 1400W, an antagonist of
iNOS, attenuated intensity of pain behaviors in CCI rats with contralateral MA
to similar levels in CCI rats without MA, and also normalized the facilitatory
effect of forskolin on excitatory synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
dorsal horn neurons in contralateral MA rats. Therefore, contralateral MA
worsened CCI-induced pain hypersensitivity probably through upregulating iNOS
and enhancing the facilitation of synaptic transmission following CCI.
Conclusion: Inhibiting the iNOS might be a potential therapeutic strategy for
concurrent OA and neuropathic pain.
Keywords: osteoarthritis, neuropathic pain, acute monoarthritis, chronic
constriction injury