108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

癌症/睾丸抗原(CTAs)在切除术后的肺癌中的表达
Authors Jin S, Cao S, Li J, Meng Q, Wang C, Yao L, Lang Y, Cao J, Shen J, Pan B, Hu J, Yu Y
Received 11 December 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2018
Published 1 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4491—4499
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S159491
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Increasing evidence shows cancer/testis antigens (CTAs) play a key
role in oncogenesis. Our pre-study finds that MAGEA1 , MAGEA10 , MAGEB2 , KK-LC-1 , and CTAG1A/B have high expression
frequencies at the protein level. We aim to explore their prognostic role and
correlations with clinical characteristics in resected lung cancer at the mRNA
level.
Methods: Thirty-eight surgical lung cancer samples were included.
Validation study was performed based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database. The
prognostic roles of CTAs were evaluated by Kaplan–Meier and multivariate
analysis.
Results: High expression of MAGEA1 (16.7%
vs 65.0%, P =0.004), MAGEA10 (61.1% vs
95.0%, P =0.016), MAGEB2 (55.6% vs 95.0%, P =0.007), and KK-LC-1 (16.7% vs
55.0%, P =0.020) was closely correlated
with lymph node metastasis at diagnosis. Patients with TNM stage II or III had
a higher expression of MAGEA10 (57.1% vs 91.7%, P =0.034) and KK-LC-1 (14.3% vs
50.0%, P =0.039) compared with patients in
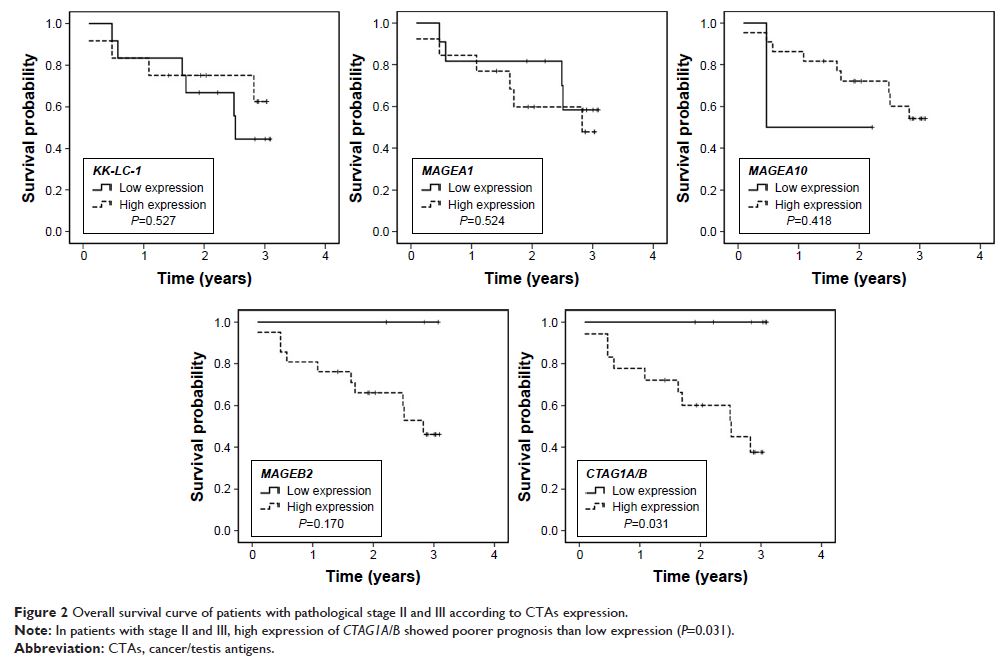
TNM stage I. High CTAG1A/B expression
showed unfavorable prognosis in all cases (P <0.05). Subgroup analysis showed
high CTAG1A/B expression was a
negative prognostic factor of survival (P =0.031) in
patients with TNM stage II or III. Although no statistical significance was
reached, high CTAG1A/B also
showed a similar prognostic trend in lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) and squamous
cell carcinoma. The Cancer Genome Atlas database showed the negative prognostic
role of CTAG1A/B was mainly induced
by CTAG1B (NY-ESO-1, P =0.047) and high CTAG1B expression (hazard
ratio =2.733, 95% CI: 1.348–5.541, P =0.005) was an
independent negative prognostic factor of lung ADC.
Conclusion: CTAs represent potential candidate targets for immunotherapy and
their expression was closely correlated with tumor stage. High CTAG1B expression was an
independent negative prognostic factor of lung ADC.
Keywords: lung cancer, cancer/testis antigens, immunotherapy, prognosis