108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二甲双胍诱导 miR-378 使 CDK1 下调,导致抑制肝细胞癌的细胞增殖
Authors Zhou J, Han S, Qian W, Gu Y, Li X, Yang K
Received 8 March 2018
Accepted for publication 12 May 2018
Published 31 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4451—4459
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S167614
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Abstract: Metformin is one of the extensively and most commonly used oral
antihyperglycemic agents, but it has been shown to exert antineoplastic effects
in many cancer cells. Recent studies have confirmed that metformin has an antitumor
effect on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the molecular mechanism
underlying this effect needs to be further studied.
Materials and
methods: CDK1 and miR-378 expression was
analyzed by western blotting and real-time PCR assays. We confirmed the
association between miR-378 and CDK1 by dual luciferase reporter assay. The
role of the miR-378/CDK1 pathway in proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis was
examined in vitro. The effect of miR-378 on HCC tumor growth was evaluated in
nude xenograft mouse model.
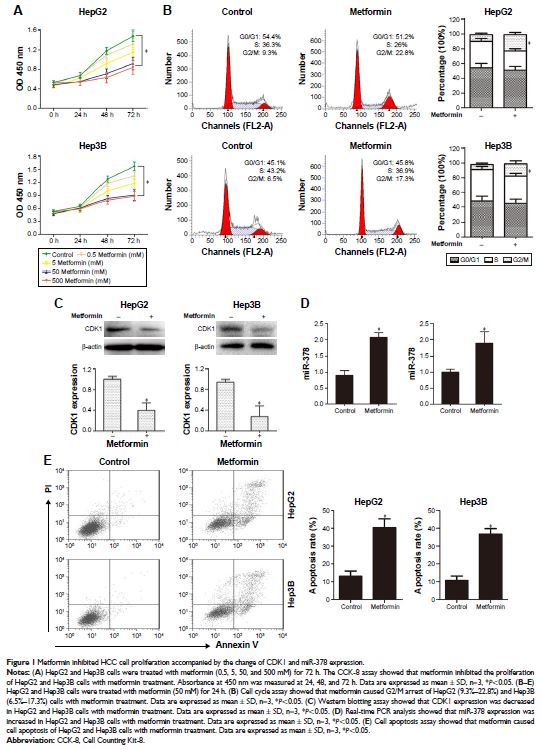
Results: Our study found that metformin significantly inhibited the HCC
cell proliferation via inducing G2/M arrest. At the same time, metformin
efficiently decreased CDK1 expression and elevated miR-378 level. Moreover, the
upregulation of miR-378 also repressed HCC cell proliferation by causing G2/M
arrest and inhibited tumor growth. Additionally, we demonstrated that miR-378
directly targeted CDK1 3'UTR and downregulated CDK1 mRNA and protein levels.
Furthermore, metformin treatment could not decrease CDK1 expression, suppress
HCC cell proliferation, and induce G2/M cell cycle arrest.
Discussion: Metformin-suppressed HCC cell proliferation was dependent on the
inhibitory effect of miR-378 on CDK1 expression. Taken together, we concluded
that metformin inhibited HCC cell proliferation via modulating miR-378/CDK1
axis.
Conclusion: Collectively, the current results provide the first evidence, to
our knowledge, that miR-378/CDK1 axis is involved in metformin modulating the
proliferation of HCC cells, which suggests a novel molecular mechanism
underlying the therapeutic effect of metformin on HCC.
Keywords: cell cycle, apoptosis, metformin, cancer, liver