108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
叶酸缀合的介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子用于增强拓扑替康在视网膜癌中的治疗功效
Authors Qu W, Meng B, Yu Y, Wang S
Received 26 May 2017
Accepted for publication 25 August 2017
Published 27 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4379—4389
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S142668
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Jonghoon Choi
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: In this study,
topotecan-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles were prepared and surface
conjugated with folic acid (FTMN) to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of
topotecan for the treatment of retinoblastoma (RB) cancers. The particles were
nano-sized and exhibited a sustained release of drug in the physiological
conditions. The folic acid-conjugated nanoformulations exhibited a remarkable
uptake in RB cells compared to that of non-targeted nanoparticles. These
results clearly indicate that receptor-mediated endocytosis is the mechanism of
cellular internalization. The greater cellular uptake of FTMN resulted in
significantly higher cytotoxic effect in Y79 cancer cells compared to that of
other formulations. The results were well corroborated with the live/dead assay
and nuclear fragmentation assay. FTMN consistently induced apoptosis of cancer
cells with an efficiency of ~58%. Our results clearly showed that
nanoparticulate encapsulation of TPT exhibited superior anticancer efficacy in
Y79 cancer cells compared to that of free drug or non-targeted nanoparticles.
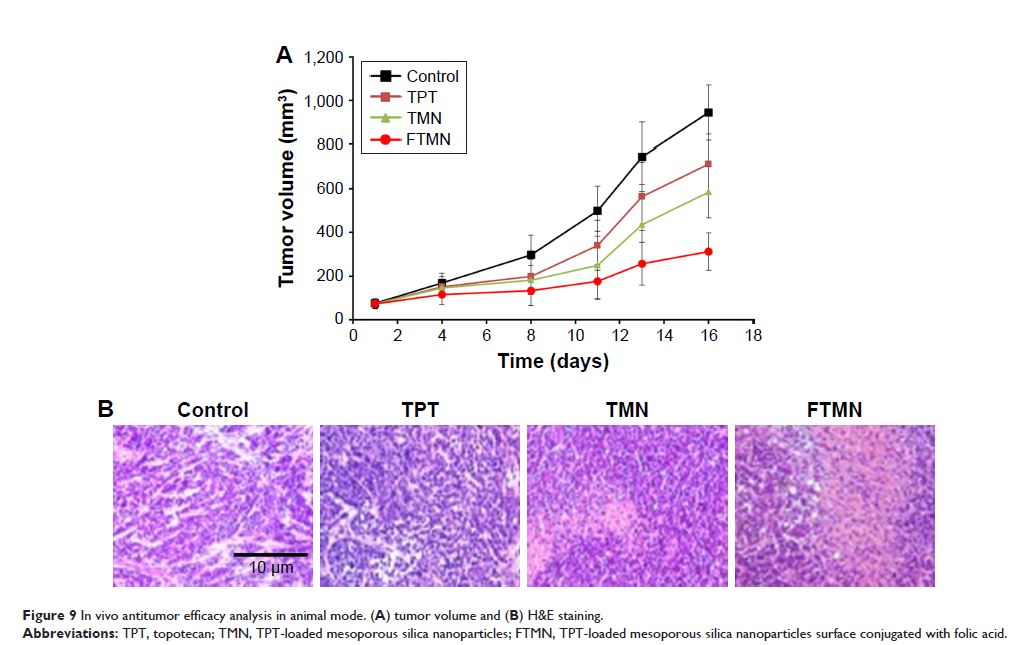
As expected, FTMN exhibited a remarkable reduction in the overall tumor volume
compared to any other group with less presence of tumor cells in histology
staining. Overall, folic acid-conjugated nanoparticulate system could provide
an effective platform for RB treatment.
Keywords: retinoblastoma, topotecan, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, apoptosis, anticancer effect
Keywords: retinoblastoma, topotecan, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, apoptosis, anticancer effect