108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

含大戟甘(Euphornin)通过诱导细胞凋亡和 G2/M 细胞周期停滞来减少人宫颈腺癌 HeLa 细胞的增殖
Authors Li XQ, Bai YL, Zhang DL, Jiao HS, He RX
Received 20 February 2018
Accepted for publication 12 May 2018
Published 27 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4395—4405
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S166018
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: The plant Euphorbia helioscopia L.
has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating various disorders
such as tuberculosis and edema. The aim of this study was to investigate the
effect of euphornin, a bioactive compound isolated from E. helioscopia , on proliferation
of human cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa cells by analyzing cell viability, rate
of apoptosis, and cell cycle progression.
Materials and
methods: The sulforhodamine B assay was used
to study the effect of euphornin on the proliferation of HeLa cells.
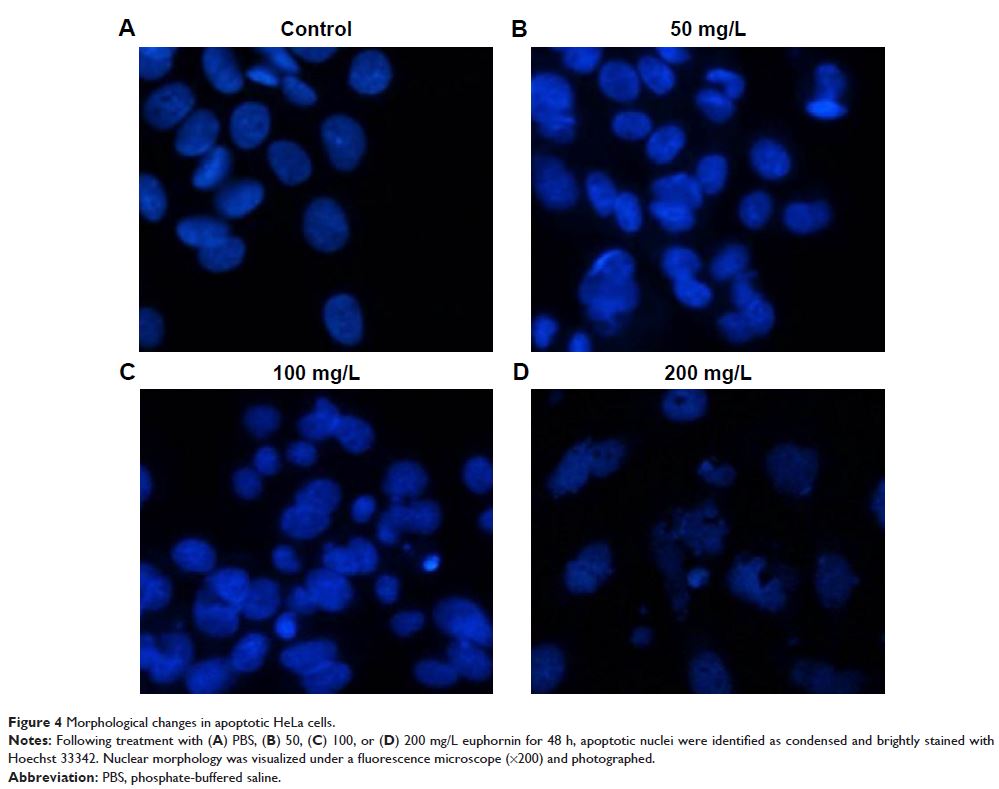
Morphological changes to cell nuclei were identified after Hoechst 33342
staining. Mitochondrial membrane depolarization (MMP) was analyzed after
staining with JC-1 dye. The influence of euphornin on the apoptosis rate was
analyzed by Annexin V/propidium iodide double staining. Fluorescence-activated
cell sorting was applied to investigate the influence of euphornin on cell
cycle progression. Proteins were obtained from HeLa cells and analyzed by
Western blots.
Results: A cell viability assay showed that euphornin inhibited proliferation
of HeLa cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. Euphornin also
induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner, with the rates of
apoptosis ranging from 25.3% to 52.6%. A high concentration of euphornin was
found to block HeLa cells at the G2/M stage. A Western blot analysis suggested
that euphornin might exhibit antitumor activity by inducing apoptosis.
Euphornin treatment altered the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 in HeLa cells, which led to
the release of cytochrome complex. The levels of cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8,
caspase-9, and caspase-10 were also markedly increased by euphornin treatment.
Analysis of cell cycles indicated that euphornin induced cell cycle arrest by
increasing the level of the phospho-CDK1 (Tyr15) protein. The various assays
demonstrated that euphornin treatment resulted in a significant suppression of
cell growth accompanied by G2/M cell cycle arrest and increased rate of
apoptosis via mitochondrial and caspase pathways.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that euphornin has the potential to be used
as a cancer therapeutic agent against human cervical adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: euphornin, cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa cells, proliferation,
apoptosis, G2/M cell cycle arrest