108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用生物信息学分析来确定食管腺癌的预后危险因素
Authors Dong Z, Wang J, Zhan T, Xu S
Received 10 November 2017
Accepted for publication 7 April 2018
Published 25 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4327—4337
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156716
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Purpose: Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) is the most common type of
esophageal cancer in Western countries. It is usually detected at an advanced
stage and has a poor prognosis. The aim of this study was to identify key genes
and miRNAs in EAC.
Methods: The mRNA microarray data sets GSE1420, GSE26886, and GSE92396 and
miRNA data set GSE16456 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus
database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and differentially expressed
miRNAs (DEMs) were obtained using R software. Functional enrichment analysis
was performed using the DAVID database. A protein–protein interaction (PPI)
network and functional modules were established using the STRING database and
visualized by Cytoscape. The targets of the DEMs were predicted using the
miRecords database, and overlapping genes between DEGs and targets were
identified. The prognosis-related overlapping genes were identified using
Kaplan–Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazard analysis based on The Cancer
Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The differential expression of these
prognosis-related genes was validated using the expression matrix in the TCGA
database.
Results: Seven hundred and fifteen DEGs were obtained, consisting of 313
upregulated and 402 downregulated genes. The PPI network consisted of 281
nodes; 683 edges were constructed and 3 functional modules were established.
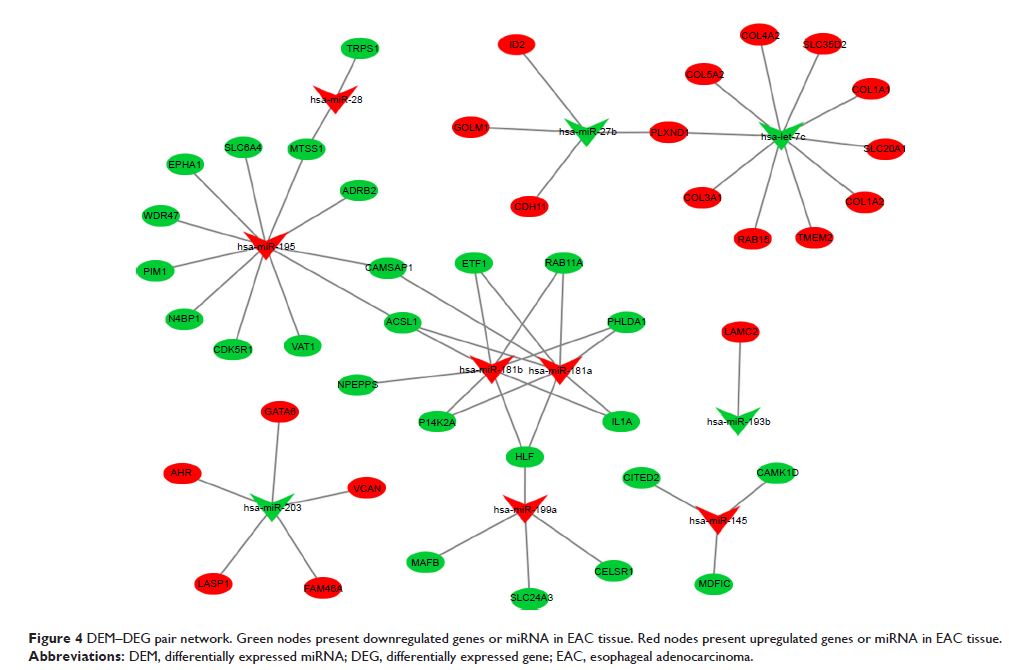
Forty-four overlapping genes and 56 miRNA–mRNA pairs were identified. Five
genes, FAM46A , RAB15 , SLC20A1 , IL1A , and ACSL1 , were associated with
overall survival or relapse-free survival. FAM46A and IL1A were found to be
independent prognostic indicators for overall survival, and FAM46A , RAB15 , and SLC20A1 were considered
independent prognostic indicators for relapse-free survival. Among them, the
overexpression of RAB15 and SLC20A1 and lower expression
of ACSL1 were also identified in
EAC tissues based on the expression matrix in the TCGA database.
Conclusion: These prognosis-related genes and differentially expressed miRNA
have provided potential biomarkers for EAC diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: esophageal adenocarcinoma, differential expression genes,
functional enrichment analysis, Kaplan–Meier analysis, Cox proportional hazard analysis