108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

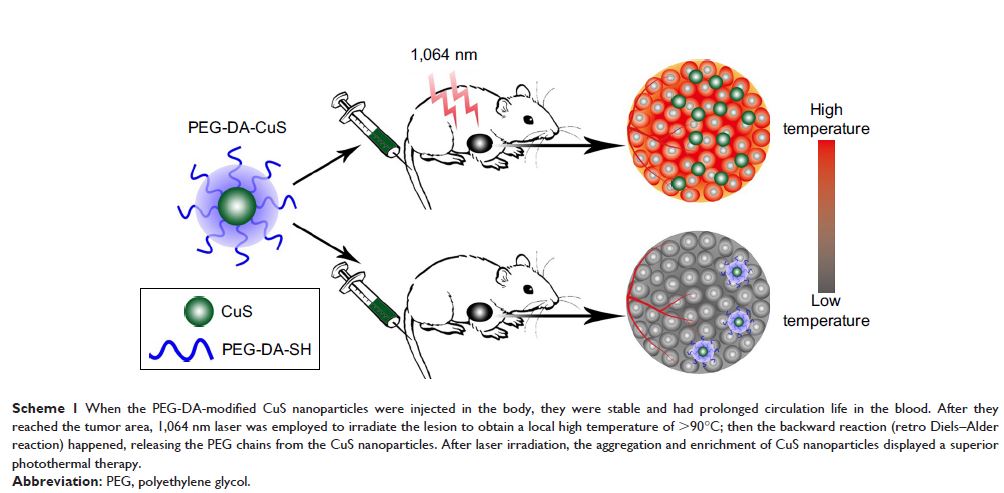
在固有的光热特性所引发的逆狄尔斯–阿尔德反应帮助下,使肿瘤中充满定制的 PEG-DA-CuS 纳米粒子
Authors Sheng J, Ma B, Yang Q, Zhang C, Jiang Z, Borrathybay E
Received 24 March 2018
Accepted for publication 25 May 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4291—4302
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S169189
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: In recent years, near-infrared laser-induced photothermal therapy
is being considered as a promising approach to kill tumors owing to its
noninvasive nature and excellent antitumor efficiency. However, the lack of
ideal photothermal agents hinders further development of this technology.
Materials and
methods: Aiming at solving this long-standing
obstacle, we report here about the polyethylene glycol (PEG)-DA modified copper
sulfide (CuS) nanoparticles (NPs) (PEG-DA-CuS NPs), a kind of semiconductor
photothermal agents that show excellent photothermal stability and high heat
conversion efficiency.
Results and
discussion: Owing to the surrounding PEG, the
water solubility of CuS NPs was significantly improved when circulating in
blood in the body. When the NPs reached the tumors and were irradiated by a
1,064 nm laser (1 W/cm2, 10 minutes), the local temperature increased above 90°C, triggering
the retro Diels–Alder reaction. After the release of PEG chain, CuS NPs soon
formed aggregates and enriched the tumor via the enhanced permeability and
retention effect, promoting the efficacy of photothermal therapy.
Conclusion: Therefore, we believe PEG-DA-CuS NPs are able to serve as a kind
of cytotoxic and efficient photothermal agent to kill cancer.
Keywords: CuS, PEG, retro Diels–Alder reaction, excellent photothermal
stability, high heat conversion efficiency, aggregation in tumor