108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于靶向光动力疗法的金丝桃素包裹的葡萄糖纳米颗粒的简易制造
Authors Shao C, Shang K, Xu H, Zhang Y, Pei Z, Pei Y
Received 1 January 2018
Accepted for publication 5 June 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4319—4331
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S161262
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yu Mi
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
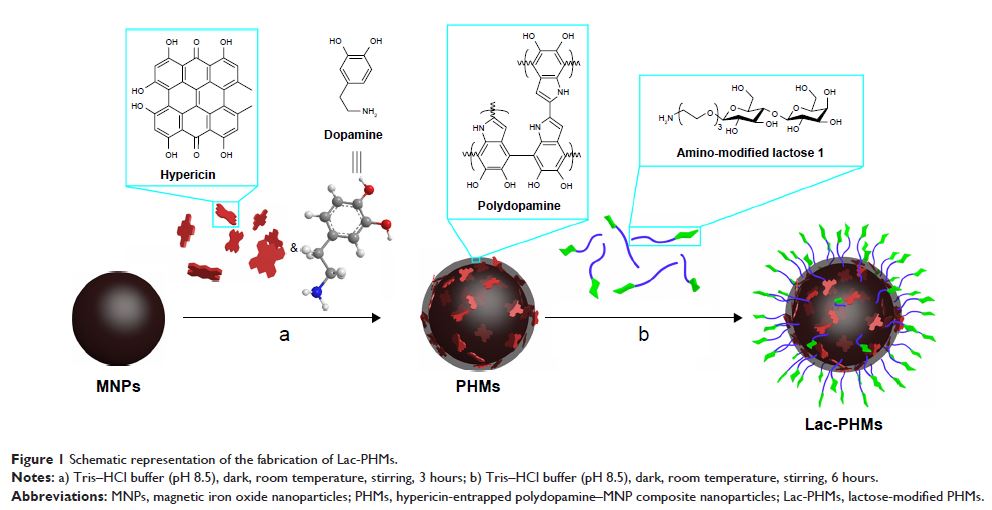
Background: Photodynamic therapy is a safe, noninvasive modality for cancer
therapy, in which the photosensitizer (PS) is a crucial component. Hypericin
(Hy) is a promising PS; however, its clinical application is significantly
limited by its poor hydrophilicity.
Materials and
methods: To overcome the clinical application
limitation of Hy, a novel strategy is developed here by entrapping Hy into
polydopamine (PDA) film formed on the surface of magnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles (MNPs) through the self-polymerization of dopamine under alkaline
condition. The amount of Hy in the Hy-entrapped PDA–MNP composite nanoparticles
(denoted as PHMs) was measured by spectrophotometry. Furthermore, lactose, as
the targeting ligand to asialoglycoprotein receptors, was conjugated to the
surface of the PHMs by taking advantage of the spontaneous reaction of PDA with
amino groups.
Results: Spectrophotometry analysis revealed that the amount of Hy in the
PHMs was 72 µmol g-1 PHMs. The fabricated Hy-entrapped glyconanoparticle (Lac-PHM) exhibited
excellent water dispersibility, stability, and selectivity for
asialoglycoprotein receptors overexpressing HepG2 cells. Atomic absorption
spectroscopy analysis showed that the amount of the Lac-PHMs taken in HepG2
cells was 2.1-fold higher than that of the triethylene glycol-modified PHMs. The
results of intracellular reactive oxygen species generation detection,
cytotoxicity study, and apoptosis detection indicated that the Lac-PHMs had a
satisfying photodynamic effect to HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: The strategy developed in this work offers great potential for
delivery of a variety of hydrophobic PSs.
Keywords: hypericin, photodynamic therapy, glyconanoparticles, targeted drug
delivery