108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超临界流体的溶液增强分散:用于处理生物材料和药物化合物的生态友好型纳米化方法
Authors Kankala RK, Chen BQ, Liu CG, Tang HX, Wang SB, Chen AZ
Received 22 February 2018
Accepted for publication 27 April 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4227—4245
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S166124
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
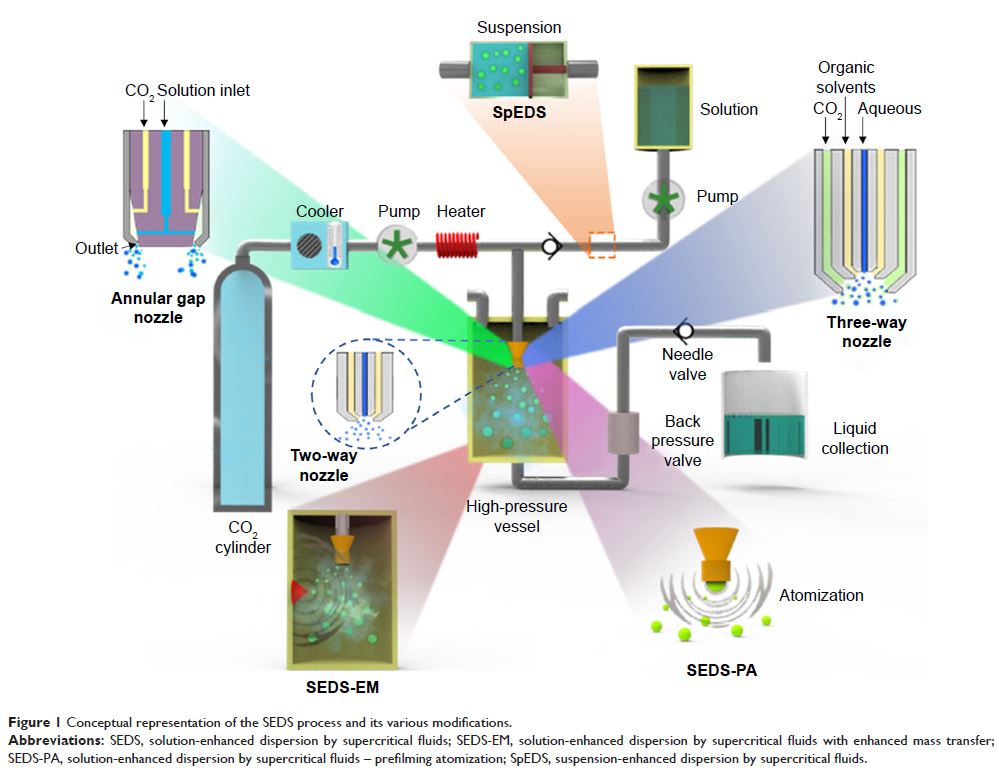
Abstract: In recent years, the supercritical fluid (SCF) technology has
attracted enormous interest from researchers over the traditional
pharmaceutical manufacturing strategies due to the environmentally benign
nature and economically promising character of SCFs. Among all the SCF-assisted
processes for particle formation, the solution-enhanced dispersion by
supercritical fluids (SEDS) process is perhaps one of the most efficient
methods to fabricate the biomaterials and pharmaceutical compounds at an
arbitrary gauge, ranging from micro- to nanoscale. The resultant
miniature-sized particles from the SEDS process offer enhanced features
concerning their physical attributes such as bioavailability enhancement due to
their high surface area. First, we provide a brief description of SCFs and
their behavior as an anti-solvent in SCF-assisted processing. Then, we aim to
give a brief overview of the SEDS process as well as its modified prototypes,
highlighting the pros and cons of the particular modification. We then
emphasize the effects of various processing constraints such as temperature,
pressure, SCF as well as organic solvents (if used) and their flow rates, and
the concentration of drug/polymer, among others, on particle formation with
respect to the particle size distribution, precipitation yield, and morphologic
attributes. Next, we aim to systematically discuss the application of the SEDS
technique in producing therapeutic nano-sized formulations by operating the
drugs alone or in combination with the biodegradable polymers for the application
focusing oral, pulmonary, and transdermal as well as implantable delivery with
a set of examples. We finally summarize with perspectives.
Keywords: controlled release, anti-solvent, nanonization, drug delivery,
polymeric carriers, parameters effect