108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

食管癌和乳腺癌中有差异表达的 circRNA 的概况
Authors Shi P, Sun J, He B, Song H, Li Z, Kong W, Wang J, Wang JM, Xue H
Received 11 March 2018
Accepted for publication 7 May 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2207—2221
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167863
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Introduction: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) function as efficient microRNA sponges
with gene-regulatory potential and are promising cancer biomarkers. In this
study, we used the Arraystar Human circRNA Array to construct a genome-wide
circRNA profile of esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC) and breast cancer
(BC).
Patients and
methods: Expression levels between cancer
lesions and adjacent normal-appearing tissues were compared. We observed 469 upregulated
circRNAs and 275 downregulated circRNAs in ESCC. Hsa_circRNA_103670 was
upregulated 20.3-fold, while hsa_circRNA_030162 was downregulated 12.1-fold.
For BC, 715 circRNAs were upregulated, and 440 circRNAs were downregulated.
Hsa_circRNA_005230 was upregulated 12.2-fold, while hsa_circRNA_406225 was
downregulated 12.4-fold.
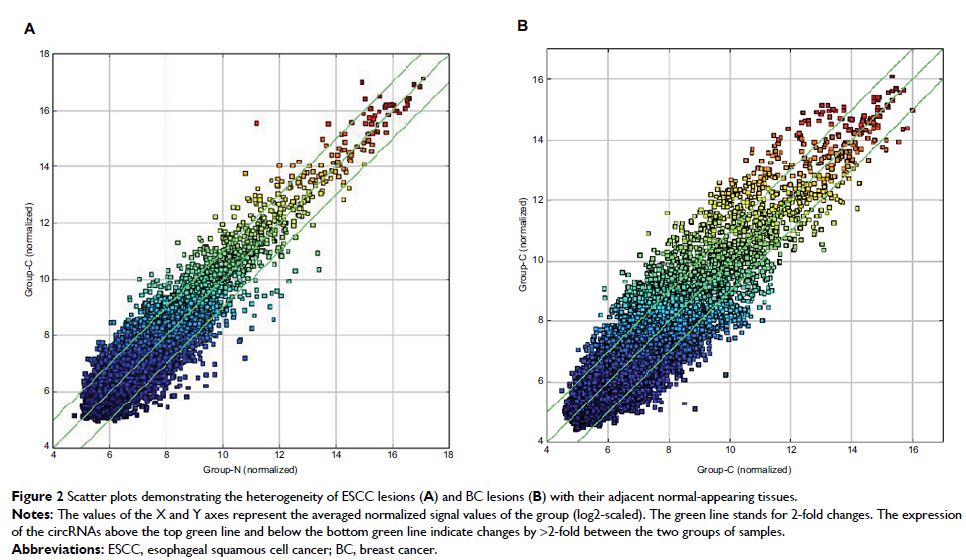
Results: When we set the criteria as fold change in expression ≥2 between
cancer and adjacent normal-appearing tissue with a P-value <0.01, there were 22
common circRNAs (11 upregulated and 11 downregulated) in relation to both ESCC
and BC. Gene ontology and the Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes analyses
showed that these circRNAs were involved in the tumorigenesis of human cancers.
Conclusion: Our study revealed that circRNAs are promising candidates as
valuable biomarkers for ESCC and BC, although relevant research is still in its
infancy and the functional role of specific circRNAs in tumorigenesis is just
starting to be elucidated.
Keywords: circRNA, noncoding RNA, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, breast
cancer, biomarker