108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HA/HSA 共同修饰的厄洛替尼 - 白蛋白纳米颗粒用于肺癌治疗
Authors Shen Y, Li W
Received 30 March 2018
Accepted for publication 7 May 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 2285—2292
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S169734
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Aim of this study was to prepare the hyaluronic acid and human
serum albumin modified erlotinib nanoparticles (ERT-HSA-HA NPs) delivery system
by a precipitation method.
Methods: ERT-HSA-HA NPs were characterized for physical properties, such as
morphology and particle size, and in vitro drug release. Moreover, the
cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, in vivo studies of ERT-HSA-HA nanoparticle were
investigated and compared in A549 cells.
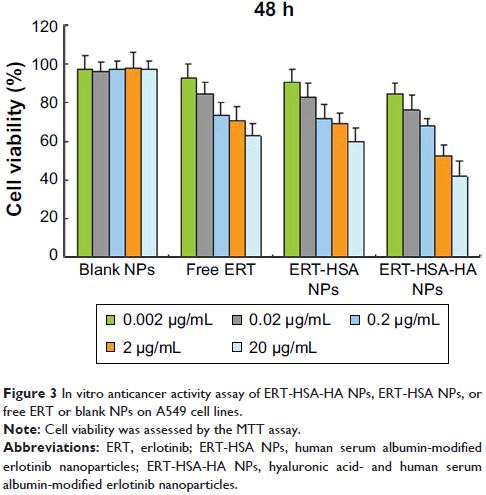
Results: The ERT-HSA-HA NPs showed spherical morphology, and their
hydrodynamic diameter was 112.5±2.8 nm. The drug loading amount and
encapsulation efficiency were 5.6% and 81.2%, respectively. After 3 months of
storage, no dramatic change, such as visible aggregation, drug content changes,
and precipitation, in the appearance of ERT-HSA-HA NPs occurred. In vitro
release showed that the release of ERT from HSA-HA NPs was slow, without
obvious burst effects at an early stage. In in vivo studies, ERT-HSA-HA NPs
showed a superior antiproliferative effect on A549 cells, and the HA
modification strategy can also facilitate the high-efficiency uptake of ERT-HSA
NPs by A549 cells. Pharmacokinetic studies showed that the form of NPs could
significantly extend the role of ERT in vivo (provided higher bioavailability).
However, there was no significant difference in the pharmacokinetic parameters
between ERT-HSA NPs and ERT-HSA-HA NPs after intravenous administration. In
terms of in vivo antitumor activity, ERT-HSA-HA NP-treated mice showed a
significantly suppressed tumor growth and no relapse after 30 d of treatment.
Conclusion: HA/HSA co-modified erlotinib albumin nanoparticles was expected to
be a new strategy in the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: erlotinib, hyaluronic acid, human serum albumin, nanoparticles, pharmacokinetic,
antitumor activity