108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在ISEcp1 介导下将负载染色体的 bla CMY-2 转导到大肠杆菌内源性 ColE1 型质粒
Authors Fang LX, Li XP, Li L, Chen MY, Wu CY, Li LL, Liao XP, Liu YH, Sun J
Received 8 December 2017
Accepted for publication 9 April 2018
Published 23 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 995—1005
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S159345
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: CMY-2 is the most prevalent pAmpC β-lactamase, but the
chromosomal bla CMY-2 gene transfer via horizontal transmission has been seldom
reported. This study aimed to describe an IS Ecp1 -mediated
transposition of a chromosomal bla CMY-2 gene from Escherichia coli into
a small endogenous ColE1-like plasmid, resulting in elevated resistance to
extended-spectrum cephalosporins.
Methods: Three ESCs-resistant ST641 E. coli strains
EC6413, EC4103 and EC5106 harbored the bla CMY-2 gene. S1- PFGE, I-ceu I-PFGE,
Southern blotting and electroporation experiments were performed to investigate
the location and transferability of bla CMY-2. The genetic context and gene expression of bla CMY-2 in the original isolates and the corresponding electroporants were
explored by PCR mapping, primer walking strategy and RT-qPCR.
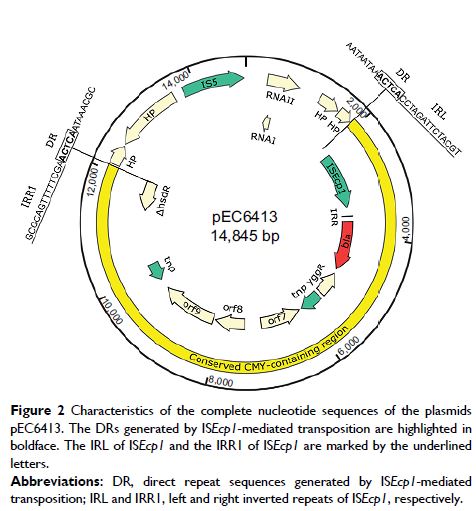
Results: The bla CMY-2-containing region (ISEcp1 -bla CMY-2-∆blc -∆yggR -∆tnp1 -orf7 -orf8 -orf9 -∆tnp2 -∆hsdR ) was transposed into endogenous ColE1-like plasmid pSC137 in the
process of electroporation at very low frequencies (10–8–10–9). The transpositions
resulted in novel larger bla CMY-2-harboring ColE1-like plasmids with size of 14,845 bp, enabling increase
in MICs of 2 to 8-fold for cefotaxime, ceftiofur, and ceftazidime in recipient
strains over their respective original counterparts. Transcriptional level
analysis revealed that the increased bla CMY-2 expression was correlated with elevated MIC values of
cephalosporins. The bla CMY-2 transposition unit was identical to that in a clinical
isolate E. coli TN44889 from France
isolated in 2004.
Conclusions: Our results firstly demonstrated that ISEcp1 mediated a transposition
of chromosome-borne bla CMY-2 into an endogenous ColE1-like plasmid by electroporation.
Amplification of the bla CMY-2 gene facilitates the strain adaptation to a changed environment with an
elevated antibiotic pressure.
Keywords: bla CMY-2, chromosome-borne, ColE1-like plasmid, ISEcp1 -mediated
transposition, extended-spectrum cephalosporin