108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
EB 病毒的环状 DNA 对结外鼻型自然杀伤/T 细胞淋巴瘤的预后意义 一项综合分析
Authors Chen RW, Wang C, Zhou Y, Wen B
Received 10 January 2018
Accepted for publication 9 April 2018
Published 20 July 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 2183—2192
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S162168
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Introduction: To evaluate the
prognostic value of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA for extranodal natural
killer/T-Cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL), we performed a meta-analysis of
published studies that provided survival information with pre-/post-treatment
circulating EBV DNA.
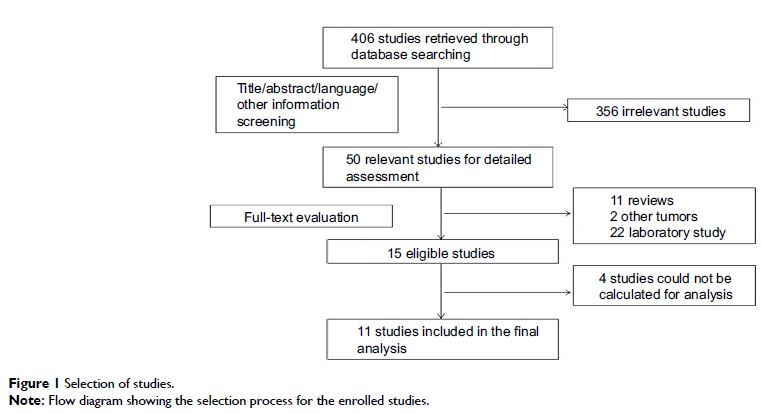
Methods: Eligible studies that discussed prognostic significance of circulating EBV DNA in ENKTL were included. Random effects models were applied to obtain the estimated hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals to evaluate prognostic significance (OS and DFS/PFS). Eleven studies covering a total of 562 subjects were included in this analysis.
Results: The summary HRs and 95% CIs of pre-treatment EBV DNA for OS and PFS/DFS were 4.43 (95% CI 2.66–7.39, P <0.00001) and 3.12 (95% CI 1.42–6.85, P =0.005), respectively. The corresponding HRs and 95% CIs of post-treatment EBV DNA for OS and PFS/DFS were 6.28 (95% CI 2.75–14.35, P <0.0001) and 6.57 (95% CI 2.14–20.16, P =0.001). Subgroup analyses indicated a strong trend of prognostic powers with pre-/post-treatment EBV DNA.
Conclusion: With the present evidence, circulating EBV DNA consistently correlated with poorer prognosis in patients with ENKTL which need further investigation in large-scale clinical studies.
Keywords: circulating EBV DNA, ENKTL, prognosis
Methods: Eligible studies that discussed prognostic significance of circulating EBV DNA in ENKTL were included. Random effects models were applied to obtain the estimated hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals to evaluate prognostic significance (OS and DFS/PFS). Eleven studies covering a total of 562 subjects were included in this analysis.
Results: The summary HRs and 95% CIs of pre-treatment EBV DNA for OS and PFS/DFS were 4.43 (95% CI 2.66–7.39, P <0.00001) and 3.12 (95% CI 1.42–6.85, P =0.005), respectively. The corresponding HRs and 95% CIs of post-treatment EBV DNA for OS and PFS/DFS were 6.28 (95% CI 2.75–14.35, P <0.0001) and 6.57 (95% CI 2.14–20.16, P =0.001). Subgroup analyses indicated a strong trend of prognostic powers with pre-/post-treatment EBV DNA.
Conclusion: With the present evidence, circulating EBV DNA consistently correlated with poorer prognosis in patients with ENKTL which need further investigation in large-scale clinical studies.
Keywords: circulating EBV DNA, ENKTL, prognosis